2G / 2.5G / 3G / 4G · 2G 2G is an abbreviation of second-generaTIon wireless telephone technology, that is, second-generation wireless communication technology. Unlike the first-generation analog signal, 2G technology has begun to use digital signals to transmit audio or other data. 2G contains two branches based on mulTIplexing multiplexing technology, one is TDMA time division multiple access technology, and the other is CDMA code division multiple access technology. GSM: established based on TDMA technology, originated in Europe, is the most widely used network in the world; · IDEN: Based on TDMA technology, there are currently two iDEN networks, operated by Nextel in the United States and Telus Mobility in Canada. · IS-136: Established based on TDMA technology, also known as D-AMPS network, with operators in the United States to build networks. · IS-95: Based on CDMA technology, also known as CDMA ONE network, mainly used in the United States and some countries or regions in Asia. · PDC: Based on TDMA technology, it is only used in Japan. · 2.5G 2.5G is a communication technology in the transitional stage from 2G to 3G. "2.5G" is not an official definition like "2G" and "3G", but is an unofficial one for subdividing 2G communication technology. statement. Generally speaking, 2.5G refers to GPRS, EDGE technology under GSM network and CDMA2000 1x-RTT standard under CDMA network. (CDMA2000 actually has two development stages, the first stage is 2G 1x-RTT standard, and the latter stage is 3G EV-DO standard). Others include EDGE or CDMA2000 1x-RTT, which have a faster data transmission rate than GPRS, in the ranks of 2.75G. Of course, this is also an unofficial definition. · 3G At present, there are mainly the following 3G standards in the world: · WCDMA: Wideband Code Division MulTIple Access, wideband code division multiple access technology, which is currently used in FOMA systems in Japan and UMTS systems in Europe. CDMA2000: This refers to the second stage of CDMA2000-EV-DO, see the content later in this article. TD-SCDMA: China's independent intellectual property rights 3G standard. · WiMAX: For details, see the back of this article. · 4G 4G is the general term for the fourth generation of mobile communication technology in the future, and there is no formal standard or technology yet. GSM · Introduction to GSM: GSM stands for Global System for Mobile CommunicaTIons. Chinese is usually translated as a global mobile communication system. It is a mobile communication network technology standard that was first used in Europe. It is also known as the 2G (2nd generation) network. The biggest feature of GSM is that it is the most popular communication standard in the world. After a survey by a specialized agency, 82% of mobile phones in the world are using the GSM network. The users come from 212 countries around the world. (The above data are from January 2007) · GSM History: In 1982, CEPT (European Conference of Postal and Telecommunications Administrations) established Groupe Spécial Mobile (predecessor of Global System for Mobile Communications) to develop a mobile communication system that can be used throughout Europe. In 1987, 13 European countries signed a memorandum of understanding and decided to cooperate in the development of a unified standard mobile communication network in Europe. In 1989, the responsibility for the development of GSM was handed over to ETSI (European Telecommunications Standards Institute). One year later, the first phase of the GSM standard was published. On March 27, 1991, the world ’s first GSM network was established in Finland by Radiolinja (Finnish communications operator, established in 1988). After two years of development, in 1993, 70 communication operators in 48 countries have established their own GSM standard mobile communication networks. · Introduction to GSM technology: The GSM network automatically searches and recognizes the user through the SIM card of the mobile phone user. The full name of the SIM card is Subscriber Identity Module, which is a chip that can record user information (such as phone book contacts). After the GSM network completes the search and identification of the SIM card, it will connect the user's mobile phone to the network and conduct voice calls or SMS text messages with other users. GSM uses a variety of voice coding, which can compress the audio with a sampling rate of 3.1 KHz to a bit rate within the range of 5.6 Kbps-13Kbps, thereby achieving synchronous voice transmission. In 1997, the GSM standard had a new development-GPRS (General Packet Radio Service) technology was integrated into the GSM network, which realized the transmission of information packets. The use of mobile phones to surf the Internet and send and receive MMS has gradually become a major development trend. In 1999, a higher-speed information transmission technology was born on the basis of GSM and GPRS. This is what we call EDGE-Enhanced Data Rates for GSM Evolution. CDMA · CDMA Introduction CDMA is the abbreviation of Code Division Multiple Access, which is what we call code division multiple access. In order to simply understand the CDMA technology, we can make an analogy: there are several people in a room that need to communicate with each other but not to confuse their identities, so that people can line up and speak to the people who want to talk in order This is the time division technology of CDMA. Or everyone faces their own conversation object to distinguish who is talking to whom. This is the frequency division technology of CDMA. CDMA mainly realizes the identification and mutual anti-interference of multiple users in the same frequency band through time division and frequency division. · The history of CDMA Speaking of CDMA, the earliest we may trace back to the period of World War II. At that time, the original intention of researching code division multiple access technology was to prevent the enemy ’s communication interference with the enemy during the war. Later, after long-term development, the United States ’ Qualcomm introduces commercial / civilian networks. In 1995, the first commercial / civilian CDMA network was successfully operated, and was quickly promoted in the Americas and Asia. China's CDMA network is currently operated by China Unicom. · CDMA technical characteristics As a spread-spectrum technology, CDMA has strong anti-interference ability, which is the original reason for the birth of CDMA technology, and is a basic feature of CDMA network. In terms of data transmission, CDMA can realize broadband transmission, and the signal has strong anti-fading ability. For communication operators, the characteristics of CDMA technology determines the high utilization rate of CDMA frequency, so it is very time-saving and labor-saving in frequency band planning. This is why we often see CDMA one-band mobile phones instead of ordinary GSM mobile phones. In that way, at least two frequency bands are supported. CDMA technology also has many advantages, so most of the global 3G standards loaded in IMT-2000 formulated by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) are based on CDMA code division multiple access technology, such as Wide-CDMA (WCDMA), CDMA2000 and China TD-SCDMA with independent intellectual property rights. It is believed that CDMA technology will also play a greater role in future communication network upgrades. HSPA · Summary HSPA is the abbreviation of High-Speed ​​Packet Access, which can be translated into high-speed data packet access / access technology. HSPA is a communication protocol built on UMTS to extend and improve existing UMTS, so we still Let's first briefly introduce the UMTS network. · UMTS UMTS stands for Universal Mobile Telecommunications System, which is a type of third-generation communication technology (3G), and it is likely that a fourth-generation communication network will be developed on the basis of UMTS in the future. UMTS was proposed by the 3GPP (3rd Generation Partnership Project, established in 1998), which is actually IMT-2000 (third-generation communication of the International Telecommunication Union (ITU)) The global standard of technology) standard is reflected in Europe. The UMTS protocol uses the Wideband-CDMA network (that is, WCDMA), so we can simply equate UMTS with WCDMA. · Introduction to HSPA Back to HSPA, HSPA currently includes two technical specifications, one is the common HSDPA technology, namely High-Speed ​​Downlink Packet Access, used to achieve high-speed downlink data transmission, the other is the rapid development in the past two years HSUPA-High Speed ​​Uplink Packet Access, used to achieve high-speed uplink data transmission. · Introduction to HSDPA HSDPA can theoretically provide a peak downstream rate of 14.4Mbps, and in terms of upstream rate, it can only reach 384Kbps at most. · Introduction to HSUPA The emergence of HSUPA meets those users who have high requirements for upload speed, and together with HSDPA constitutes a complete HSPA technology. HSUPA can provide a theoretical peak upload rate of up to 5.76Mbps. Currently, communication operators that have established HSUPA networks around the world can basically provide peak upload rates of 1.5-2.0Mbps for mobile terminals that support HSUPA technology. EV-DO / LTE / HSOPA / WiMAX · EV-DO EV-DO is an abbreviation of Evolution-Data only, is a 3G broadband data transmission standard, and belongs to the large family of CDMA2000 specifications. CDMA2000 originally used 1xRTT technology in the 2.5G communication era. After entering the 3G communication era, a new member was born in the CDMA2000 family-EV-DO. EV-DO was first proposed by Qualcomm in the United States and officially released in 1999. At that time, it was to meet the IMT-2000 global 3G standard formulated by the International Telecommunication Union. At present, the EV-DO network is mainly used in the United States, and can provide users with a theoretical downlink peak rate of 3.1 Mbps and a theoretical uplink peak rate of 1.8 Mbps. · LTE The full name of LTE is Long Term Evolution, which is a long-term development and evolution plan for 3G networks by the 3GGP organization. LTE can provide a data transmission rate far exceeding that of any existing 3G network in the future. The most important technical standard in the process. At present, major communication operators around the world are actively preparing for the construction of LTE networks. For example, we have reported in the article two days ago that the famous communication operator Vodafone is expected to fully launch the LTE network after 2011, while Nokia, Seven well-known communication companies in the world, such as Sony Ericsson, have also reached an agreement on the construction of an LTE intellectual property licensing framework. · HSOPA HSOPA stands for High Speed ​​OFDM Packet Access, OFDM is the abbreviation of Orthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing, that is, orthogonal frequency division multiplexing technology, and some people have translated it as orthogonal frequency division multiplexing technology. Its main idea is: divide the channel into several positive Cross sub-channels, convert high-speed data signals into parallel low-speed sub-data streams, and modulate to transmit on each sub-channel. Because OFDM is a data transmission protocol with a design idea completely different from CDMA, HSOPA is not established based on WCDMA technology like HSDPA and HSUPA, so it is not a member of the HSPA family. HSOPA is part of the LTE plan proposed by 3GPP, also known as Super 3G, which can theoretically provide a peak downlink rate of up to 100Mbps and an uplink peak rate of 50Mbps, which is much higher than HSPA technology. Currently, HSOPA is under development. · WiMAX The full name of WiMAX is Worldwide Interoperability for Microwave Access. It is a new multi-mode long-distance wireless data transmission standard that can realize point-to-point data transmission and mobile phone access data transmission. WiMAX is based on the IEEE 802.16 standard, also known as WirelessMAN. The WiMAX standard was established by the WiMAX Forum. The WiMAX Forum was established in June 2001 and is dedicated to the globalization of WiMAX standards and WiMAX research and development cooperation. WiMAX is a new member of the International Telecommunication Union's IMT-2000 global 3G standard. Like WCDMA, CDMA2000 (Phase 2), and TD-SCDMA, it belongs to the officially certified third-generation communication technology. OLED Module,OLED Display Module,1.3 Inch OLED Display ESEN Optoelectronics Technology Co., Ltd, , https://www.esenlcd.com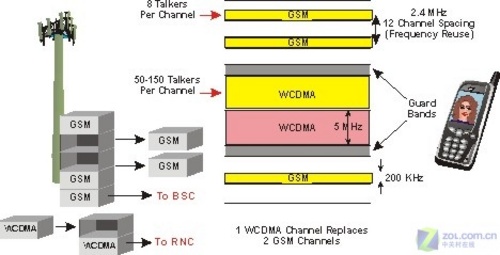
Many netizens report that in some articles, a lot of communication professional terms have appeared. Although there is a general understanding of these terms, the concept of many things is still relatively vague. Today, the Zhongguancun online mobile channel, in response to the requirements and needs of readers and friends, brings you an article that explains common communication terms, hoping to bring some help to readers and friends. The place also invites readers and friends to criticize and correct.
Worldwide, 2G mainly includes 5 standards: 
3G is the third-generation mobile (wireless) communication technology now in full swing. In order to achieve communication, cooperation, universalization and unification of communication technologies in the world, the International Telecommunication Union has established a global universal standard that regulates 3G technology-IMT -2000. 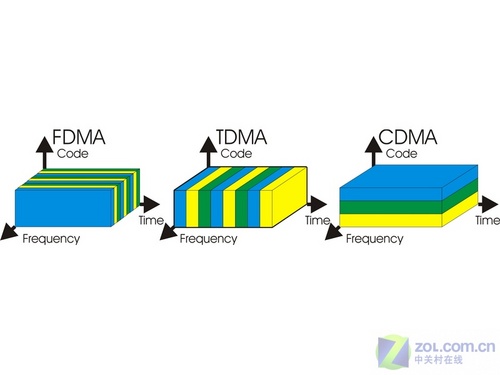
The principle of CDMA technology is based on spread spectrum technology, that is, the information data with a certain signal bandwidth to be transmitted is modulated with a high-speed pseudo-random code with a bandwidth much larger than the signal bandwidth, so that the bandwidth of the original data signal is expanded and then modulated by the carrier wave. Send it out. The receiving end uses the exact same pseudo-random code to perform correlation processing with the received bandwidth signal, and then replaces the broadband signal with a narrow-band signal of the original information data to despread to realize information communication. 
Because HSPA is built on the UMTS 3G standard, it is also called HSDPA as the 3.5th generation communication system. At present, a total of 211 HSDPA networks have been established in 90 countries around the world, providing users with a high-speed network with a theoretical downlink peak rate of 3.6Mbps or higher and 7.2Mbps.
2G to 4G GSM to WiMAX common communication terms
2G to 4G GSM to WiMAX common communication terms