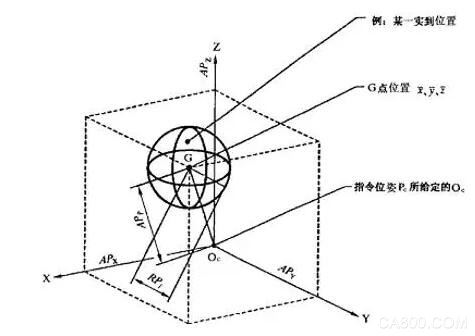
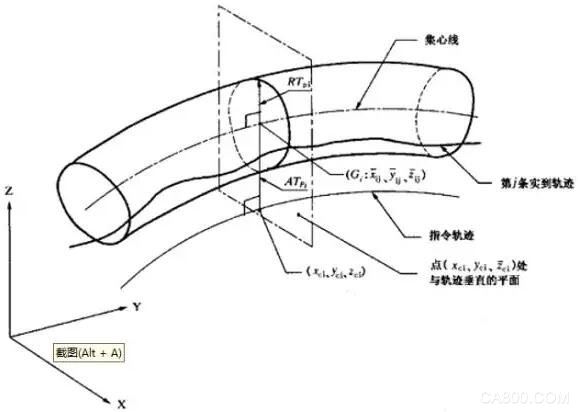
2016 is not simple! In this year, the robotics industry has achieved rapid development. From the Spring Festival party on the Spring Festival of the monkeys to the colorful robot dance to the now blooming robot operating systems, control systems companies, from robot conferences across the country, robot forums to robots and Internet operations, big data and other emerging technologies, We were amazed to discover that robots are no longer “big dumb bears†that would only repeat manual labor, but are increasingly intelligent and personalized. Nowadays, more and more robots have entered the "people" enterprises. The enterprises are also celebrating the "small 99" in their hearts. What is the performance of the robot's control system? At present, there is no industry-specific performance test standard for industrial robot control systems. In the robotics industry, performance specifications are generally mentioned for the entire machine. There are many indicators to evaluate the overall performance of industrial robots. Based on different design purposes and applications, the whole machine parts, structure design and parameter adjustment are also different. The control system is only one of the links, the engine (servo motor), variable speed Boxes (reducers), chassis/suspensions (structures), etc. have a great influence on the overall performance of the robot. Therefore, to do a robot's performance test is still very complicated. However, the national standard “GB/T 12642 - 2001 Industrial robot performance specifications and test methods†has defined standards for more than a dozen robots' performance indicators, among which three are often mentioned: repeatability, pose accuracy, Track accuracy. So, what kind of good would we like to test the robot's control system alone? In general, the performance of an industrial robot control system can be expressed indirectly by the robot's pose and track accuracy. Pose Accuracy The pose accuracy of a robot generally refers to the pose repeatability. The posture of the robot refers to the pose of the robot with respect to a certain reference coordinate system. The repeat position accuracy is one of the most important technical indicators of the robot. The index reflects the electromechanical performance and the use effect of the robot, that is, the robot pair is the same. Instruct the pose to repeat the response from the same direction n times to achieve the same degree of pose. The laser tracker is generally used to measure the pose accuracy, as shown in the following figure: To achieve higher pose accuracy, the control system is required to provide the following functions: ◠Compensation for kinematic parameter errors of mechanical linkages, such as connecting rod machining errors, assembly errors, mechanical tolerances, etc.; ◠compensate for joint flexibility and link flexibility; ◠Provides highly accurate mechanical zero calibration. Path Accuracy The trajectory accuracy of a robot generally refers to the trajectory repetition accuracy, which indicates the degree of consistency of the actual trajectory when the robot repeats the same trajectory command n times. A laser tracker is also generally used for testing, allowing the robot to repeat a certain trajectory n times, and then take the radius of the cross section of the trajectory composed of n trajectories. As shown below: Model Based Control is now generally used to improve track accuracy. ABB compared the Quick Move to the True Move, and after using the model control, the robot can maintain a very high trajectory consistency at any speed allowed by the system. In addition, to achieve high trajectory accuracy, it is also necessary to perform joint friction compensation for the robot. After a simple understanding of how to detect the performance of the robot control system, do you feel it suddenly? Power Breadboard,Breadboard Power Supply,Breadboard Power Supply Module,Breadboard Power Module Cixi Zhongyi Electronics Factory , https://www.zypcbboards.com