The high temperature and high pressure steam is circulated and cooled, so that the heat around the evaporator in the cabin is taken to the condenser outside the cabin and is radiated to the atmosphere. Pressure Controller,Digital Pressure Controller,Air Pressure Controller,Pneumatic Pressure Controller Shenzhen Ever-smart Sensor Technology Co., LTD , https://www.fluhandy.com
Both the refrigerated evaporator and the heated radiator are installed in the air conditioning case under the front wall of the cab. The air conditioner has an external air inlet and a return air outlet. The cold air or hot air generated by it is blown to the driver's head, feet, windshield glass, glass through six adjustable wind direction and air outlets. Other air outlets include instrument panel air outlets, floor air outlets, and defrosting air outlets.
Except for the maximum cooling state (MAX) and the stop state (OFF) for the internal air circulation state, the normal circulation (NORM), ventilation (VENT), hot air (HEAT), and defrosting states are external circulation.
The warm air supply is to take in the external air and heat it, and then mix it with the external cold air in different amounts to reach the required supply air temperature. The heat source of the warm air is the hot water that cools the engine. This part of the hot water passes through a water valve to dissipate the heater radiator in the cab.
The air-conditioning supply is performed by an evaporator in the air conditioner to cool and dehumidify the externally intruded air, and then mix with the hot air to reduce the indoor temperature. The evaporator works not only in the cold air but also in the defrosting state if necessary.
The air conditioner control panel is equipped with a blower switch 41. The rotational speed of the blower motor 43 is achieved by varying the size of the blower resistor 42. There is a temperature limit switch on the blower resistor. When the temperature reaches 149 °C, it must be disconnected. At this time, the high gear must be used directly.
The so-called refrigeration process is to take low-temperature and low-pressure refrigerant vapor (for example, Freon at 0 °208M Pa at the °C, ie RI2 steam) into the refrigeration compressor, and compress it into a high-temperature and high-pressure gas (for example, 70 ° C, the pressure is 1·4 MPa of Rl2 steam). The high temperature and high pressure Freon steam is exothermic to the atmosphere in the condenser outside the cabin, because the high temperature and high temperature refrigerant temperature (70 ° C) is much higher than the atmospheric temperature (such as 40 ° C), if the cooling agent R12 becomes 60T after cooling The liquid, while releasing a large amount of heat of condensation, while the pressure is still 1.4 MPa, the liquid high-temperature refrigerant is dehumidified and buffered by a receiver drier to supply liquid to the expansion valve at a relatively stable pressure and flow rate. The liquid refrigerant is throttled and depressurized by the expansion valve, and is vaporized by heat in the evaporator. The air-conditioner blast motor continuously sucks the air in the cabin that needs to be cooled into the air conditioner shell, blows through the heat absorbing tube of the evaporator and the heat absorbing sheet, and transfers the heat in the air to the refrigerant of the evaporator. The refrigerant absorbs heat and vaporizes, thereby absorbing a large amount of heat in the cab, that is, heat of vaporization. The vaporized refrigerant is again sucked by the compressor, compressed
The amount of cooling depends on the amount of vaporization of Rl2 in the evaporator, which is controlled by the compressor operating time and the expansion valve opening. Whether or not the compressor is operating is determined by its own electromagnetic clutch 44, which operates when the electromagnetic clutch combines the compressor shaft with the compressor pulley (which is coupled to the crankshaft pulley via a V-belt). When the temperature in the cabin is higher than a certain value, the temperature sensing package located at the outlet of the evaporator causes the temperature switch 46 to turn on the compressor electromagnetic clutch by the expansion of the internal liquid volume, so that the compressor pushes the Rl2 cycle, and the temperature of the evaporator drops to a certain temperature. A value, the temperature package shrinks, so that the temperature control switch disconnects the electromagnetic clutch circuit of the compressor, then the compressor pulley can only idle and does not work.
The opening of the expansion valve is used to regulate the flow rate of the refrigerant and the pressure of Rl2 to the evaporator. A variable throttling gap is formed between the ball valve spool of the expansion valve and the mating surface of the conical valve seat, and a temperature sensing bellows filled with the expansion liquid is arranged on the upper portion of the valve core, and the refrigerant vapor pressure under the diaphragm is The spring acts to balance the diaphragm. The temperature rise or fall in the cabin causes the temperature-sensitive membrane box to expand or contract, thereby changing the downward pressure of the ball-end valve spool, that is, changing the flow rate of the refrigerant, so as to ensure that the evaporator performance is fully utilized when the temperature is high. It also prevents the wet compression of the compressor when the temperature is low.
The table is the normal pressure value of each part of the air-conditioning system of Chevrolet at different temperatures, for reference during maintenance.
Table: Normal pressure values ​​for various parts of the air conditioning system at different temperatures 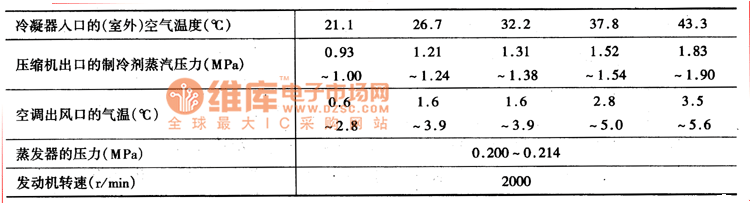
Note: l. The above table is the test value of the Chevrolet sedan or station wagon air conditioning system with a wheelbase of 2.95m.
2. The quality of the refrigerant is 1.698kg.
3. The temperature and humidity increase, the load of the airborne system increases, and the pressure increases.