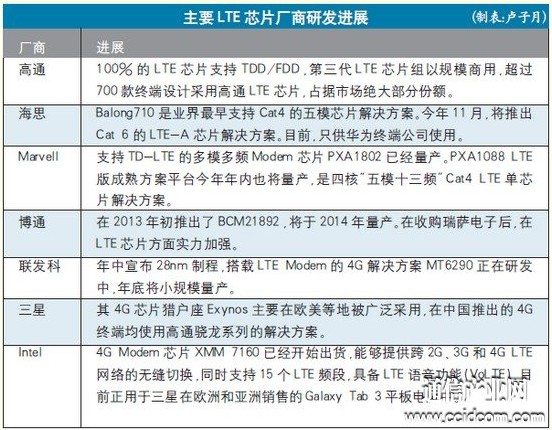
Recently, Beijing Mobile officially launched two 4G contract mobile phones, which once again detonated people's enthusiasm for 4G. Prior to this, China Mobile's TD-LTE network has entered the stage of scale-up testing, and the network is now ready for commercial use. Therefore, the development of TD-LTE terminal chips will determine whether China's 4G can really enter people's lives. At this stage it is difficult to support large-scale commercial According to the development law of the communication industry, the development and promotion of terminal chips need to go through a long process. First of all, the pre-development investment of a chip is huge, and no manufacturer is willing to act rashly without seeing the market clearly. Second, compared to system equipment, terminal chips are more sensitive to technological upgrades and evolution. For system equipment, the evolution of technology is often just adding a board, and for chips, it is necessary to push the original product back. Therefore, in the development of 2G and 3G, the development of terminal chips lags behind the development of the network. Although it conforms to the industry's development laws, this situation also has disadvantages: in the initial stage of network commercialization, the terminal chips are immature, which affects users' enthusiasm for the network. This has been reflected in the highly competitive 3G period. In the early stages of TD-SCDMA network commercialization, due to the immature terminal chips and poor user experience, many users have lost confidence in TD-SCDMA. With this lesson in mind, China Mobile has always emphasized the importance of the development of the TD-LTE full industry chain, and proposed the "five-mode ten-band" and VoLTE technology development route, striving to point out clear directions for chip manufacturers. However, even so, today's commercially available TD-LTE chips are still rare. In addition to Qualcomm, HiSilicon, Marvell can provide mass production chips, most chip manufacturers are still in the development and sample stage. This also directly affects the development of TD-LTE terminals. Currently, there are only more than ten mobile phones supporting TD-LTE worldwide. In the mobile hall of Beijing Mobile, in addition to two mobile phones that can be sold, there are only three other mobile phones for display. Obviously, the TD-LTE chip has not yet entered the period of mass production. There is also a certain distance to support the commercial use of TD-LTE. In this regard, Shi Guang, director of the academic work department of the China Communications Society and secretary-general of the TD Technology Forum, said that there are very few manufacturers that can provide large-scale commercial chips, and it is not enough to support large-scale commercial use. If large-scale commercial use is required, multiple chip manufacturers are required to supply them. This is not only a question of the number of chips. Only one or two chip manufacturers supply, terminal manufacturers will feel at risk. Technology is accessible, licensing is important There are many factors that affect the development of chips. The first is the industry's hunger for chips. Dr. Zhang Lu, Director of Marvell Mobile Products, said that at present, LTE is developing rapidly in the US and Japan markets. At the same time, Europe, the Middle East and other places will also set off a wave of LTE wide coverage this year. The global LTE network deployment speed is very fast, and the intensity is also very large. Judging from the current situation of the two major US operators, Verizon and AT & T, 100% of the newly released terminals are LTE terminals. Since the user experience of LTE is very good and user demand is strong, the terminal is also showing explosive growth and will continue to be applied. This is the future trend. Zhang Lu predicts that in China, many manufacturers will soon launch LTE smart terminals, and the demand for LTE chips will also increase significantly. In 2014, mass-production of LTE chips for Chinese operators will be realized. Another key factor that will affect the development of TD-LTE chips is the issuance of 4G licenses. The issuance of 4G licenses will undoubtedly stimulate the enthusiasm of chip manufacturers. In this regard, Time said that the timing of the issuance of 4G licenses is particularly important. It takes a while for the maturity of the chip to be tested to find the problem. Therefore, you can't wait until the chip can be commercialized on a large scale before you issue a license. To select an appropriate node, early commercial start-up, poor terminal experience, and late commercial start-up will delay the development of the industry. In terms of technology that people are more concerned about, TD-LTE chips are progressing smoothly. The 28nm process has become popular, and many chip manufacturers have begun to make 20nm chips. Multi-mode multi-frequency is not a technical problem for larger manufacturers. It will take some time to reach the "five-mode ten-frequency" proposed by China Mobile. Most TD-LTE chips can already support Cat4 capability, and some products can support Cat6 capability through carrier aggregation technology. Supporting VoLTE will also become standard equipment for TD-LTE chips. Time said that TD-LTE chip technology no longer has unpredictable difficulties, and currently only needs time to improve. He emphasized that in addition to the research and development of chip hardware, it is also crucial for the development of software and overall solutions. The importance and difficulty of software development is no worse than hardware. Qualcomm leads, saves variables in the future The development of TD-LTE is inseparable from the support of chip manufacturers. However, from 2G, 3G to LTE, the supply pattern of the entire terminal chip is gradually converging. From the operator to the equipment manufacturer to the chip manufacturer, the number of upstream manufacturers decreases. Industry experts said, "Upstream manufacturers need to share the money with downstream manufacturers. However, investing in a chip is not less expensive than investing in a device. Once the downstream manufacturer has a problem, the upstream manufacturer collapses faster than the downstream." In the brutal market competition, in the LTE era, there are fewer and fewer manufacturers involved in chips. For TD-LTE, which has a relatively weak industrial chain, the support of chip manufacturers is precious. Currently, 17 chip manufacturers have launched or are developing LTE TDD / FDD fusion multi-mode chips. Qualcomm, HiSilicon, Marvell and other manufacturers have launched five-mode chips. Throughout the TD-LTE chip market, Qualcomm plays a pivotal role. 100% of Qualcomm's LTE chips can support both TDD and FDD. As of March 2013, there are 700 terminal designs that use Qualcomm ’s LTE chips. According to the latest report from ABI Research, Qualcomm ’s LTE baseband chip shipments accounted for more than 2/3 of global shipments in 2012. At present, in Qualcomm's QRD plan, the MSM8930, MSM8926 and MSM8928 chipsets of the Snapdragon 400 series all support LTE-TDD / FDD and support 3G / 4G multi-mode multi-frequency. Hisiligen's Balong710 is the industry's first TD-LTE / FDDLTE / TD-SCDMA / WCDMA / GSM five-mode chip solution that supports Cat4. In November this year, HiSilicon will launch a Cat 6 LTE-A chip solution with a download speed of 300Mbps. Currently, HiSilicon's terminal chips are only used by Huawei terminal companies. In addition, Marvell's multi-mode multi-frequency Modem chip PXA1802 has been mass-produced. At present, the PXA1802 has been used in a variety of terminal forms. The ZTE U9815 mobile phone equipped with PXA1802 has become one of the first smartphones in China to obtain a TD-LTE network license in August. . Many other manufacturers are also developing LTE mobile phones based on PXA1802. At the same time, Marvell's PXA1088 LTE version of the mature solution platform will also be mass-produced this year. It will be the industry's first quad-core "five-mode 13-band" Cat4 LTE single-chip solution for the mass market. Broadcom also made efforts in the LTE field in 2013. BCM21892 was launched in early 2013. It can support FDD-LTE, TD-LTE, HSPA +, TD-SCDMA, GSM, etc., and will be mass produced in 2014. After acquiring Renesas Electronics, Broadcom strengthened its strength in LTE chips. In addition, Samsung, MediaTek, Intel, Lianxin Technology and other manufacturers will also become strong competitors in the field of LTE chips. Time said that the early TD-LTE chip market pattern does not represent the future market. Many manufacturers like to work hard in the future. According to the experience of TD-SCDMA, there are still many variables in the future market pattern. Remote Training Collar,Pet Trainer Dog Training Collar,Remote Control Dog Training Collar,Stimulation And Vibration Remote Training Collar Elite-tek Electronics Ltd , https://www.aetertek.ca