Linear power supply, switching power supply difference The adjustment tube of the linear power supply works in an amplified state, so the heat generation is large and the efficiency is low (about 35%). It is necessary to add a bulky heat sink, and also requires a large-sized power frequency transformer, when multiple voltage outputs are to be produced. The transformer will be bigger. The regulating tube of the switching power supply operates in saturation and cut-off state, so the heat generation is small, the efficiency is high (more than 75%) and the large-volume transformer is omitted. However, the DC output of the switching power supply will be superimposed with a large ripple (50mV at 5V output typical), and the Zener diode can be improved at the output end. In addition, since the switching tube works, it will generate a large spike interference. The magnetic beads are connected in series in the circuit for improvement. Relatively speaking, the linear power supply has no such defects, and its ripple can be made very small (below 5mV). Switching power supplies are preferred where power efficiency and installation volume are required. Linear power supplies are often used where electromagnetic interference and power purity are required (eg, capacitive leakage detection). In addition, when the circuit needs to be isolated, most of the DC-DC is used to supply power to the isolated part (DC-DC is the switching power supply from its working principle). Also, the high-frequency transformer used in the switching power supply may be troublesome to wind up. The switching power supply and the linear power supply are completely different in internal structure. As the name suggests, switching power supply has a switching action. It uses variable duty ratio or frequency conversion to realize different voltages. The implementation is more complicated, and the biggest advantage is high efficiency. More than 90%, the disadvantage is that the Wenbo and switching noise is large, suitable for occasions where the requirements of Wenbo and noise are not high; while the linear power supply has no switching action, which belongs to continuous analog control, the internal structure is relatively simple, and the chip area is also small. The cost is lower, the advantage is low cost, the noise of the ripple is small, and the biggest disadvantage is the low efficiency. They each have their own shortcomings that complement each other in application! Second, the principle of switching power supply: The switching power supply mainly includes an input power grid filter, an input rectification filter, an inverter, an output rectification filter, a control circuit, and a protection circuit. Their function is: 1. Input grid filter: Eliminate interference from the power grid, such as motor start, electrical switch, lightning strike, etc., and also prevent high-frequency noise generated by the switching power supply from spreading to the power grid. 2. Input rectifier filter: rectify and filter the input voltage of the grid to provide DC voltage to the converter. 3. Inverter: It is a key part of the switching power supply. It converts the DC voltage into a high frequency AC voltage and acts to isolate the output from the input grid. 4. Output rectification filter: Rectify and filter the high-frequency AC voltage outputted by the converter to obtain the required DC voltage, and also prevent the interference of high-frequency noise on the load. 5. Control circuit: Detects the output DC voltage and compares it with the reference voltage for amplification. The pulse width of the oscillator is modulated to control the converter to keep the output voltage stable. 6. Protection circuit: When the switching power supply has an overvoltage or overcurrent short circuit, the protection circuit stops the switching power supply to protect the load and the power supply itself. The switching power supply rectifies the alternating current into direct current, converts the direct current into alternating current, and rectifies the output into the required direct current voltage. This switching power supply eliminates the transformer in the linear power supply and the voltage feedback circuit. The inverter circuit in the switching power supply is completely digitally adjusted, and can also achieve very high adjustment accuracy. The main advantages of switching power supply: Small size, light weight (20 to 30% of volume and weight of linear power supply), high efficiency (generally 60 to 70%, and linear power supply is only 30 to 40%), strong anti-interference, wide output voltage range, Modular. The main disadvantages of switching power supplies: Due to the high frequency voltage generated in the inverter circuit, there is some interference to the surrounding equipment. Need good shielding and grounding 3. The secondary of the switching transformer induces a high-frequency voltage, which is supplied to the load through rectification and filtering; 4. The output part is fed back to the control circuit through a certain circuit to control the PWM duty cycle to achieve the purpose of stable output. When the AC power input is input, it generally passes through something like the Erectochrone to filter out the interference on the grid, and also filters out the interference of the power supply to the grid. When the power is the same, the higher the switching frequency, the smaller the volume of the switching transformer. However, the requirements for the switching tube are higher; the secondary of the switching transformer can have multiple windings or one winding with multiple taps to obtain the required output; generally, some protection circuits, such as no-load, short-circuit, etc., should be added. Otherwise, the switching power supply may be burned out. The above is the general working principle of the switching power supply. In fact, there is already a dedicated chip with very high integration, which makes the peripheral circuit very simple and even free of debugging. For example, the TOP series of switching power supply chips (or modules) can be made into a basic switching power supply with a few RC components and a switching transformer. Switching Power Supply & Linear Power Supply The main working principle of the switching power supply is that the Mos tube of the upper bridge and the lower bridge are turned on. First, the current flows through the upper bridge Mos tube, and the storage function of the coil is used to concentrate the electric energy in the coil, and finally the upper bridge Mos tube is closed, and the lower part is opened. The bridge's Mos tube, coil and capacitor continue to supply power to the outside. Then turn off the lower bridge Mos tube, then open the upper bridge to let the current enter, and then repeat, because the Mos tube is to be turned on, so it is called the switching power supply. Pharmaceuticals,2-Methyl- Propanoic Acid Monohydrate Price,2-Methyl- Propanoic Acid Monohydrate Free Sample,Pure 2-Methyl- Propanoic Acid Monohydrate Zhejiang Wild Wind Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. , https://www.wild-windchem.com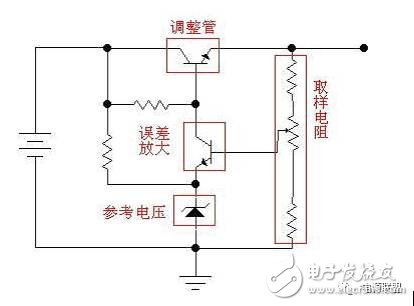



What is the difference between a linear power supply and a switching power supply?
The DC power is different according to the requirements. The linear power supply is best to output linear DC power. It can be used in high requirements. The switching power supply is second. It is a transformer and switch tube with high switching speed. It is characterized by weight. Small, large capacity, high output quality, phase control power is used in occasions where the requirements are not high and the current is very large.