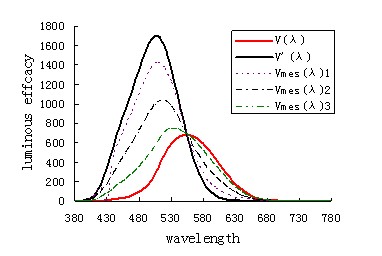
For decades, the establishment of an effective system for intermediate visual photometry has been a topic of interest to the international lighting community. Recently, the International Commission on Illumination (CIE) Technical Committee TC 1-58, which is based on the "visual function in the middle vision range", completed its work and introduced a visual photometric-based intermediate photometric recommendation system, which was officially released by CIE. Technical Report CIE 191:2010 [1]. This technical report fills the gap in the relevant photometric standards and will bring challenges and impacts to previous lighting systems based on bright visual photometry, and will have a major impact on the development and application of LEDs as future light sources. CIE is the most authoritative international organization in the field of lighting and ISO recognized international standardization organization. A photometric system can only be accepted and applied internationally if it is approved and recommended by CIE. The intermediate visual brightness area refers to the area where the brightness is between bright and dark vision, and the intermediate visual brightness level is generally considered to be in the range of 0.001 to 3 cd·m-2. The intermediate visual illumination includes road and street lighting, outdoor lighting and other night traffic lighting. The human visual efficiency function V mes (λ) and the visual human visual efficiency function V(λ) in the intermediate vision are different. As shown in Fig. 1, the visual optometrist is based on the brightness matching, and the nighttime illumination measurement based on the bright visual photometric V(λ) does not accurately react into the light efficiency of the human eye. The newly released CIE191:2010 is based on the human visual function, that is, the completion of visual tasks: recognition, detection, reaction time, etc. to establish spectral sensitivity functions. It has been used by many relevant international organizations and many countries in the past few decades. The results of a large amount of research work, China's Chongqing University, Fudan University and other universities and research institutions have also made a lot of contributions [2,3]. Figure 1 The visual efficiency function of the human eye In the intermediate vision area, the spectral sensitivity of the human visual system is not static, it varies with the degree of illumination. This is caused by a change in the number of rod-shaped cells and cone-shaped cells acting on the retina. Therefore, only one intermediate visual spectral sensitivity function is not sufficient. We need a series of functions and a detailed description of the series of functions used in photometry. The spectral optical efficiency function Vmes(λ) described in the new intermediate vision system (such as V mes (λ) 1, V mes(λ) 2, V mes(λ) 3) in Fig. 1 is the bright visual spectrum. A linear combination of the optical efficiency function V(λ) and the dark visual spectral luminous efficiency function V'(λ). When applying intermediate visual photometry, the background brightness and the S/P value derived from the spectral data of the source are required as the input quantity, and the S/P value is the ratio of the dark visual light output to the clear visual light output, and the S/P value of the light source. The higher the light efficiency in the intermediate visual design. The rate ngshi using the intermediate vision system to measure will change the luminosity output of the lamp, which in turn changes the light efficiency level of the lamp. Most of the current "white light" sources used in road lighting have S/P values ​​between about 0.65 (such as high pressure sodium lamps) and 2.5 (such as some metal halide lamps). The warm white LED has an S/P value of about 1.15, and the cool white LED has an S/P value of about 2.15. When the new intermediate vision system is used to calculate these white light sources under different ambient brightness, the apparent light effect will change significantly. For example, when the brightness of the visual visuality is 1 cd·m-2, the variation of the S/P value between 0.5 and 2.5 is between 5% and 15% after using the recommended intermediate visual luminosity system, and the brightness of the visual vision is 0.3. When cd·m-2, the amount of change is between -10% and +30%. With the rapid development of the LED industry, LED is gradually entering the lighting market. In particular, LEDs can be used to create a wide range of spectral characteristics, providing a new solution for a wide range of intermediate vision applications. At the same time, the introduction of the CIE intermediate vision photometric system also provides a basis for LED manufacturers to optimize the development of LEDs for low-brightness lighting applications, which has a major impact on the development and application of LEDs as future light sources. Intermediate visual photometry favors white light sources with high S/P values. The use of intermediate visual design lighting can also achieve good color rendering, which is expected to further pave the way for white LED applications in outdoor lighting. The new intermediate visual photometric system should be fully put into practical use. On the one hand, it needs a series of targeted intermediate visual lighting design application guidance methods. On the other hand, it is also important to promote the measurement of intermediate visual luminosity in industry and users. At present, the second division of CIE has established the Technical Committee TC 2-65 "Photometric Measurement in the Vision of the Middle Vision". Intermediate visual photometric instruments must consider the actual spectral sensitivity of different visual levels. China's distant companies, Fudan University and other units are almost in sync with international advanced theory and standardization [4], and have done a lot of research and development work in this area. The equipment can meet the basic needs of intermediate visual photometry. It is believed that with the international consensus of intermediate vision, intermediate vision will soon be applied to various fields of lighting, especially in the field of transportation and road lighting. The milestone progress of intermediate vision will also be brought to LED and other lighting industries and enterprises. Come to unlimited opportunities. references [1] CIE191:2010 Recommended System for Mesopic Photometry Based on Visual Performance [2] Chen Zhonglin, Hu Yingkui. Study on the maximum value of optical performance in intermediate vision. Journal of Chongqing Jianzhu University. 2008 30(4) 15-18 [3] Cao Yang, Lin Yandan, Application of Visual Function Method in Road Lighting. Journal of Lighting Engineering. 2005 16(4) 44-49 [4] Zheng Jinchuan, Yao Qi, Li Qian, Lin Yandan. Development of intermediate vision equivalent illumination conversion module. Proceedings of the 2008 Annual Lighting Technology Forum, Yangtze River Delta Lighting Technology Forum and Shanghai Lighting Society 2008 Annual Meeting.