First, the definition: Pull-up is to clamp the indeterminate signal through a resistor at a high level! The resistor acts as a current limiting device at the same time! Pull down the same reason! Pull-up is to inject current into the device, pull-down is output current; weak strength is only the resistance of the pull-up resistor is different, there is no strict distinction; for non-collector (or drain) open circuit The ability of the output circuit (such as the ordinary gate circuit) to boost the current and voltage is limited. The function of the pull-up resistor is mainly to output the current channel of the open collector output type circuit. Second, the pull-down resistor function: 1. Increase the voltage level: a. When the TTL circuit drives the COMS circuit, if the high level of the TTL circuit output is lower than the lowest level of the COMS circuit (typically 3.5V), then it is necessary to The output of the TTL is connected to a pull-up resistor to increase the value of the output high level. b. The OC gate must be equipped with a pull-up resistor to increase the high value of the output. 2, increase the drive capability of the output pin , and some of the microcontroller pins often use pull-up resistors. 3, N / A pin anti-static, anti-interference: In the COMS chip, in order to prevent damage caused by static electricity, the unused pins can not be suspended, generally connected to the pull-up resistor to reduce the input impedance, providing a relief path. At the same time, the pins are suspended and it is easier to accept external electromagnetic interference. 4, resistance matching, suppressing reflected wave interference: resistance mismatch in long-line transmission is easy to cause reflected wave interference, plus pull-down resistor is resistance matching, effective suppression of reflected wave Disturb. 5. Preset space state / default potential: Connect or pull down the resistors on some CMOS inputs to preset the default potential. When you do not use these pins, these inputs Pull down to 0 or pull up to 1. On a bus such as the I2C bus, the idle state is obtained by the pull-up resistor. 6. Improve the noise margin of the chip input signal: if the input terminal is in a high-impedance state, or the high-impedance input terminal is in a floating state, you need to add pull or pull down to avoid receiving Random levels affect the operation of the circuit. Similarly, if the output is in a passive state, it needs to be pulled or pulled down, for example, the output is only the collector of a triode. Thereby improving The noise margin of the chip input signal enhances the anti-jamming capability. {The power-to-component pull-up resistor acts as a pull-down resistor that normally causes the pin to go high to the component. The function is to make the pin low-level pull-up resistor and pull-down. The range of resistance is determined by the device (we generally use 10K) +Vcc -Gnd In general, the role of pull-up or pull-down resistors is to increase the current and enhance the drive capability of the circuit. For example, the p1 port of 51 Also, the p0 port must be connected to the pull-up resistor before it can be used as an io port. The difference between pull-up and pull-down is one for sinking current and one for sinking current. Generally speaking, the sinking current is larger than the current drawn. That is, the current sinking drive capability is stronger} Third, the selection principle of the pull-up resistor value includes: 1. It should be large enough to save power and the current sinking capacity of the chip; the resistance is large and the current is small. 2. It should be small enough to ensure sufficient driving current; the resistance is small and the current is large. 3. For high-speed circuits, excessive pull-up resistors may flatten the edges. Considering The above three points are usually selected between 1k and 10k. Similar to the pull-down resistor Fourth, the principle: The pull-up resistor is actually the load resistor of the collector output. Regardless of the switch application and analog amplification, the choice of this resistor is not a head shot. Work in a linear range More to say, here is the discussion that the transistor is a switching application, so only talk about the switching method. Find a TTL device data separately, look at the final level, and there is load inside. The resistance is different according to different driving ability and speed requirements. The low-power resistance value is large, and the fast resistance value is small. But chip makers have a hard time meeting the needs of the application. There may be many kinds of the same kind of function chip, so simply do not do this load resistance, and the user can freely choose the external connection, so the chip with OC and OD output appears. by In digital applications, the transistor operates in the saturation and cut-off regions, and the load resistance is not high. The resistance value is as small as long as it is not small enough to damage the final transistor. Time can meet the design requirements, just choose one to work properly. But the details of whether a circuit design is good or not are also considered. Collector output switching The circuit is always on whether it is on or off. When the transistor is turned on, the current flows from the load resistor to the ground through the transistor. When the transistor is turned off, the current is input from the load resistor through the load. Blocking the ground, if the load resistor selects a small point, the power consumption will be large, which is to be avoided in the system design of battery power supply and low power consumption. If the resistor is large, it will be taken. The delay of the rising edge of the signal, because the input capacitance of the load is charged by the passive pull-up resistor on the rising edge, the larger the resistance, the longer the rise time, and the falling edge is through the active crystal. Body tube discharge, the time depends on the device itself. Therefore, when selecting the pull-up resistor value, the designer should balance the power consumption and speed according to the actual situation of the system. 3. From the perspective of IC (MOS process), explain the input/output pins separately: 1. For the chip input pin, if it is suspended on the system board (not connected to any output pin or driver), it is dangerous. Because it is very likely that the input capacitor internal charge charge is accumulated at this time. Bring it to an intermediate level (such as 1.5V), so that the PMOS and NMOS transistors of the input buffer are turned on at the same time, thus forming a direct path between the power supply and the ground, resulting in Large leakage current can damage the chip for a long time. And because it is at the intermediate level, the internal circuit will judge the logic (0 or 1). Connect the pull-up or pull-down resistor. After that, the internal point capacity is charged (discharged) to the high (low) level, and the internal buffer is only turned on by the NMOS (PMOS) tube, which does not form a DC path from the power supply to the ground. Damage is caused, because the protection circuit is usually added in the design of the chip pin, but it is not necessary.) 2. For the output pin: 1) Normal output pin (push-pull type), it is generally not necessary to connect pull-up or pull-down resistors. 2) OD or OC (open drain or open collector) type pins, This type of pin requires an external pull-up resistor for line and function (multiple outputs can be directly connected at this time. Typical applications are: INT (interrupt signal) output of multiple chips on the system board) Connect directly, then connect a pull-up resistor, and then input the INT pin of the MCU to implement the interrupt alarm function). Its working principle is: Under normal operating conditions, the NMOS transistor inside the OD-type pin is turned off, and it is in a high-impedance state for the external, and the external pull-up resistor causes the output to be at a high level (invalid interrupt state); When there is an interrupt demand, the NMOS transistor inside the OD pin is turned on, because its on-resistance is much smaller than the pull-up resistor, so that the output is at a low level (active interrupt state). For MOS The resistance of the pull-down resistor on the circuit is preferably tens to hundreds of K. (Note: This answer does not involve chips in the TTL process, nor does it consider the effects of impedance matching, electromagnetic interference, etc. when designing high-frequency PCBs.) 1. The pull-up or pull-down resistor indicated on the pin of the chip refers to a resistor or equivalent resistor designed inside the pin of the chip. The purpose of designing this resistor is to eliminate the need for the user. To use the function of this pin, you can set this pin to the default state without adding components. It will not make the CMOS input floating. Please pay attention to this if you use it. The value is not what you want, you should connect this input directly to the state you need. 2. If this pin is pulled up, it can be used for "line or" logic. Externally open-drain or open-collector output of other chips. Form negative logic or input. If it is pull-down If it is, it can form a positive logic "line or", but the external connection can only be a high-level open-drain chip output of CMOS. This is because the CMOS output is high and low. The drains of the PMOS and NMOS give current and can be made as P-leak open or N-leak open. The high level of TTL is output current by the source follower, not suitable for "line or". 3, TTL to CMOS drive or vice versa, in principle, it is not recommended to use a pull-down resistor to change the level, it is best to add a level conversion circuit. If the power supply on both sides is 5 volts, you can straight Successive but affects performance and stability, especially when CMOS drives TTL. When the logic levels on both sides are different, it is necessary to use level conversion. When the power supply voltage is 3 volts or less, it is not recommended. It is even more difficult to pull the level with a resistor. 4, chip external resistance is determined by the application, but it is not feasible to use the resistor to pull the level or improve the driving ability in the logic circuit. Need to improve the driver should add the drive circuit. The level change should be added to the level conversion circuit. There are special chips including long line reception. Automotive Push Button Switches
Automotive Push Button Switches
Automotive Push Button Switches, also called Push Button Starter Switch, is one kind of switches to turn on the car. As for the Automotive Switches , we have Automotive Push Button Switches, Automotive Toggle Switches, Automotive Rocker Switches, Automotive Rotary Switches and Automotive Battery Switches for our customers to choose.
The Starter button switches mainly based on the car button switch. The main function is to start the car, switch on the car power supply or start the car internal equipment. The automotive starter switch is mainly based on DC current and voltage, and has a wide range of dimensions. The installation size ranges from 8.5mm to 22mm directly.
Our push button switches can be matched with the dust proof and waterproof cap. When the car equipment is working in a harsh environment, our Yeswitch car start button switch could still be regularly used.
Our variety of Automotive Momentary Push Button Switch, can match different colors and different appearances of dust-proof and waterproof caps, dust-proof and waterproof grade can reach IP67 grade. Along with excellent electrical life times, high load current and voltage, our Yeswitch start button switch is not limited to automotive field , heavy machinery, and ships are also widely recognized by customers.
Automotive Push Button Switches,Antique Push Button Switch,Micro Push Button Switch,Mini Push Button Switch YESWITCH ELECTRONICS CO., LTD. , https://www.yeswitches.com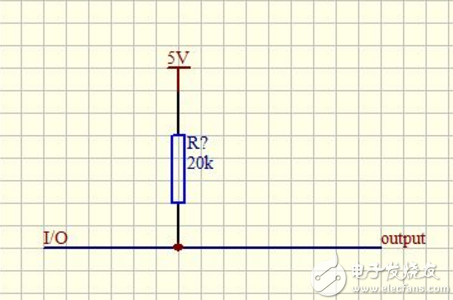
+------+=Pull-up resistor
|+-----+
|Component|
|+-----+
+------+= Pull-down resistor

