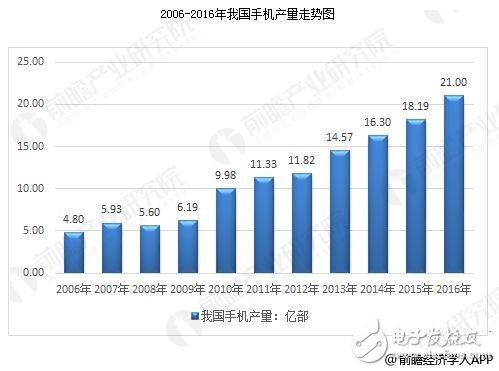
As the world's largest smartphone market, China's smartphone sales in the first quarter of 2018 fell below 100 million for the first time, down 21% year-on-year, continuing the decline since the second half of last year. "Now many domestic smartphone manufacturers have adopted the business strategy of 'maintaining domestic survival and developing overseas'." Communications industry analyst Liu Xudao told reporters that India and Southeast Asian countries are currently in the stage of popularization of smart phones, and demand for mobile phones is large. . According to data from the Prospective Industry Research Institute's "China Mobile Phone Market Prospects and Investment Forecast Analysis Report", in 2014, the overall output of China's mobile phones reached 1.63 billion units, a year-on-year increase of 6.8%. In 2015, the industry produced 1,819 million mobile phones. In 2016, the domestic mobile phone market produced 2.10 billion units. In the past five years, in terms of domestic mobile phone production data, in 2016, China’s mobile phone production growth rate increased. From 2012 to 2015, China’s total mobile phone production increased, but the growth rate was Slowing down year by year, China's mobile phone production growth rate returned to double digits in 2016. In 2017, China's total smartphone shipments were 459 million units, down 4% year-on-year. Especially in the fourth quarter, smartphone shipments were only 113 million, down 14% year-on-year. In 2017, shipments in China's smartphone market saw declines for the first time in 12 months. From this point of view, the battlefield of smart phones in China has gradually approached the ceiling, and the development of the industry has basically entered the post-development stage. In China's smart phone market, there will be a decline in shipments. The main reason comes from two aspects. First, after experiencing the wave of exchanges in 2016, the mobile phone market is basically in a saturated state. Relevant data shows that in 2016, the popularity of mobile phones in China has reached 97%, and the distribution rate of smartphones has reached 74%, which has led to a decrease in the demand for smartphones in 2017. Second, the quality of smartphones The technical aspects such as functions and functions are constantly improving, and the periodicity of people changing mobile phones is constantly increasing. According to data released by the international research institute GFK, in 2017, Huawei ranked first in the Chinese smartphone market with a sales volume of 102 million units, and its market share accounted for 23%. OPPO won the runner-up with a sales volume of 77.56 million units, and its market sales accounted for 17%. The third place is the sales volume of 72.23 million units, with a market share of 16%, and Apple and Xiaomi both ranked fourth with a market share of 11%. The five mobile phone brands alone accounted for 78% of the Chinese smartphone market. Nowadays, the pattern of domestic smart phone brands such as Xiaomi, Huawei and OPPO has basically been settled in the Chinese market. The Chinese smartphone market has steadily developed. Liu Xudao said that from the above various data, it can be seen that the development of domestic smart phones in China has been difficult to break through. In order to gain more market share and earn more profits, it is imperative to seek development overseas. In 2017, the outstanding performance of domestic smart phone manufacturers in overseas markets, especially in India and Southeast Asia, to some extent offset the unfavorable factors caused by the lack of performance and market saturation in the domestic market. Wang Yanhui, secretary general of the China Mobile Alliance, pointed out that the Southeast Asian South Asian market is so attractive to Chinese mobile phone brands that it is reflected in the following two aspects: First, the South Asian mobile phone market in Southeast Asia is mainly based on social channels, and the telecom operators are not as powerful as the US market. The competition is relatively open; second, international brands like Apple are relatively weak in Southeast Asia, resulting in relatively equal opportunities for other manufacturers. Under this trend, many Chinese manufacturers have already begun to expand the Southeast Asian market. Many Chinese smartphone manufacturers have achieved rapid growth in several key markets in the region. Xiaomi will build three new foundries in conjunction with Foxconn in India, and the millet factory will reach six. This will greatly improve the production capacity of Xiaomi mobile phone and Mijia's entire intelligent products. OPPO and Huawei, which have formed a standing position with Xiaomi in India, are also likely to continue to follow up. Previously, OPPO invested 1.5 billion yuan in an industrial park in Noida, India, at the end of 2016, including a manufacturing plant. OPPO increased its budget to 2.26 billion yuan in December 2017, apparently wanting to increase production lines. To increase production capacity. Together with Huawei, the top four domestic mobile phones have built factories in India. In the Southeast Asian market, IDC's 2017 Southeast Asia smartphone market report shows that the top five domestically produced mobile phones occupy three seats, namely OPPO, vivo and Huawei. OPPO and Huawei, like last year, still maintain the second and fourth place. In 2016, Asus, which ranked third, fell out of the top five and was replaced by vivo. It should be noted that with the warming of the Southeast Asian mobile phone market, the shipments of the three domestic mobile phones are gradually increasing. Among them, the growth rate of vivo was as high as 118.2%, OPPO also increased by 29.3%, and Huawei increased by 3.8%. The market share of the three domestic mobile phones is 29.8%, which has surpassed the number one Samsung by 29.3%. At the same time, domestic mobile phones such as Coolpad and Lenovo are also very popular in Southeast Asia. In the reality that the domestic smartphone market continues to decline in 2018, the overseas market is clearly the biggest hope for domestic growth in performance. At the same time, it is worthy of all manufacturers to invest heavily, and it is necessary to further expand the battlefield and get out of India and Southeast Asia. For the global market, the pursuit of a broader market space. When China's mobile phones are leaping forward in Southeast Asia, some Southeast Asian mobile phone brands are declining. According to Nair, a senior analyst at the market research firm Strategy AnalyTIcs, one of the main features of the Southeast Asian mobile phone market is the strength of local smartphone manufacturers, especially in Indonesia, the Philippines and Thailand, but in recent years, most of them have already Faced with pressure from foreign manufacturers. Against the background of increasingly fierce smartphone competition, many local local brands have turned their attention to function machines. “In the case of Indonesia, the largest smartphone market in Southeast Asia, OPPO and Xiaomi’s market share occupied the second and fourth positions respectively in the third quarter. OPPO sales increased by 163% year-on-year, and millet sales increased by 233%. Nair said, "In the similar markets of the Philippines, Thailand, Malaysia and Vietnam, several Chinese mobile phone brands have entered the top five." In this regard, Wang Yanhui said: "I believe that in the next two years in the Southeast Asian market will be Chinese brands and Samsung brands in PK, this situation has emerged in India." Samsung is still the dominant player in the Southeast Asian smartphone market. In 2016, Samsung's smartphone market share in Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Singapore, Thailand and other Southeast Asian countries exceeded 30%. However, in recent years, with the steady movement of Chinese brand mobile phones such as Huawei, OPPO, and vivo in the Southeast Asian market, Samsung has indeed faced tremendous pressure of “dropping powderâ€. According to the 2017 Southeast Asia smartphone market report released by market research organization IDC, OPPO's market share reached 17.2%, followed by the first Samsung (29.1%), vivo (7.2%) and Huawei (5. 4%) ranked third and fourth, and Apple ranked fifth with 4.4%. The market share of the three Chinese brands has surpassed Samsung, which is the first time in the Southeast Asian smartphone market. The data proves that in Southeast Asian countries, Chinese brand mobile phones have become "star products." However, while enjoying the praise of Southeast Asian consumers, there are also comments that the majority of Chinese mobile phone brands in the local market are "given by the low-end machines." OPPO and vivo are difficult to compete with Samsung and Apple in the high-end machine market. Although Huawei has been committed to the development of the mid-to-high-end machine market, it has entered the Southeast Asian market late, so it can only be tied with Samsung in the high-end machine market. ", there is still a gap with Apple.
Anisotropic magnets are magnets whose magnetization directions in the magnets are aligned in a certain direction.
Magnet powder for anisotropic magnets is composed of a single crystal or polycrystal with an aligned direction of magnetization in one magnet particle. When a magnetic field is applied externally during molding (this magnetic field is called an aligning magnetic field), the magnet powder moves to align with the direction of the magnetic field and is solidified in an aligned state, resulting in an anisotropic magnet. Magnet powder aligned with an aligning magnetic field is solidified with keeping magnetization. Therefore, after removing the alignment magnetic field, the molded body becomes a magnet having a magnetic force. Anisotropic Ferrite Magnets,Pump Magnet,Cooler Pump Magnet,Submersible Pump Magnet HU NAN YUBANG MAGNETIC MATERIAL CO.,LTD , https://www.ybmagnet.com