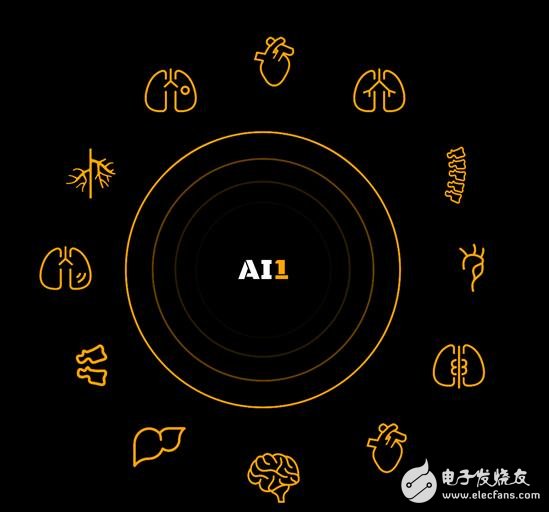
The arrival of the intelligent era, considered to be the fourth industrial revolution, has made the words artificial intelligence (AI) and big data a topic that people often discuss after dinner. With the emergence, progress, intersection and integration of various technologies, many new disciplines are emerging and gradually applied to the medical and health fields. 90% of medical data comes from medical imaging, and medical imaging data is growing at an annual rate of 30% year-on-year. In contrast, the growth rate and productivity of imaging doctors are insufficient to cope with such growth trends. This will put tremendous pressure on the doctor. On the other hand, most of the current medical image data still needs manual analysis. The most obvious defect is inaccuracy. The judgment based on experience is easy to cause misdiagnosis. Artificial intelligence relies on powerful image recognition and deep learning technology, which will solve two major problems in the manual processing of medical image big data, greatly improve the efficiency and accuracy of data analysis, reduce the pressure on doctors, and improve the efficiency of diagnosis and treatment. And accuracy. Zebra Medical Vision, based in Kibbutz Shefayim, Israel, is a company that uses machines and deep learning to deliver the next generation of products and services to the healthcare industry. Its imaging analysis platform enables healthcare organizations to identify patients at risk and provide improved, preventive treatment pathways to improve patient care. Save doctor costs Zebra's platform provides a cloud-based, fully managed development environment. A large number of desensitized research data and data are available. The platform features advanced GPU (graphics processor) computing power and supports a wide range of research tools. Different research organizations can also collaborate through this platform to create tools together. Zebra's Radiation Assist System receives scanned images from a variety of modules, automates analysis, and interprets clinical findings. The results found by the system are provided to the radiologist, other physician or hospital system in real time as needed. Using a proprietary database, Zebra uses machine learning technology to develop software that analyzes data in real time with manual interpretation accuracy, providing the radiologist with the necessary assistance to properly manage the ever-increasing workload without sacrificing quality. . At the same time, medical providers use Zebra to predict disease. Zebra tells them that patients have a high risk of cardiovascular disease, lungs, bones and other diseases. In addition, Zebra has led to the establishment of a number of medical regulations, such as the Medical Services Accessibility and Child Health Insurance Program Reauthorization Act (MACRA). With Zebra, healthcare professionals are able to give patients the attention they need at the right time, saving not only the overall cost, but also the quality of care. AI1 program: one dollar for detecting high-risk diseases Zebra's AI1 program helps users automatically detect high-risk disease, and costs $1 per scan. The current program covers disease detection in bone, lung, cardiovascular, liver and other parts. 1) Bone density algorithm Zebra's bone density algorithm uses tomographic images to obtain bone density, and the resulting value is equivalent to the T value of bone density measured by the Dual Energy X-Ray Absorption Method (DEXA). Health care providers can use existing tomographic data to pre-screen patients with high fracture risk without the need for additional testing or radiology procedures. The results can be used in bone health or fracture prevention programs, which in turn reduces the overall proportion of fractures and associated expenditures. One-third of women over the age of 50 and one-fifth of men have osteoporosis, and more than 9 million fractures worldwide are associated with osteoporosis each year. In addition, 80% of potential patients are undetected or untreated, and the quality of life of patients with osteoporotic fractures is greatly degraded – 25% of hip fractures are admitted to nursing homes within 12 months of fracture. . In the United States alone, the cost of osteoporosis treatment is estimated to reach $17 billion. One of the indicators used to determine whether a patient has osteoporosis is bone density. The DEXA measurement yields a T value, plus other risk factors to know the possibility of osteoporosis. However, only a few people will actively monitor their bone density, and only a few people have done DEXA measurements, so the proportion of osteoporosis is always low. 2) Compression fracture algorithm Zebra's Compression Fracture Detection Algorithm combines traditional machine vision image segmentation and convolutional neural network (CNN) techniques for any tomography scan of the chest, abdomen, and pelvis. The algorithm can automatically segment the spine image, identify and locate compression fractures, and distinguish between compression fractures, endplate degeneration and bone spurs. Compression fractures: Osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures are common, and one in four menopausal women is affected, and one in seven men over 65 is affected. Vertebral compression fractures (VCF) are a direct cause of reduced mobility and functional status, especially in elderly patients. Timely surgical or minimally invasive surgery for vertebral compression fractures is very effective, but few people do so. There are many causes of vertebral compression fractures, such as infection, trauma, malignant tumors, osteoporosis, etc. Among them, osteoporosis is the most important cause. Therefore, in people over 50 years old, vertebral fractures become an indicator of osteoporosis. 3) Fatty liver algorithm If found to be timely, fatty liver is reversible through adjustments in lifestyles such as diet, exercise, and alcohol intake. Zebra's fatty liver algorithm analyzes thoracic/gastric tomographic data, automatically segmenting the liver and calculating its average density in the image. This algorithm can be used as a warning bell for pre-diabetes to drive lifestyle changes. 4) Emphysema algorithm Zebra's emphysema algorithm analyzes images of thoracic tomography, detects areas of pulmonary emphysema, and calculates the volume of emphysema in the overall lung volume. In addition, Zebra can provide a more accurate understanding of the population prevalent in specific emphysema, helping patients manage disease properly and effectively before the situation worsens. Nearly 12 million people in the United States have been diagnosed with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease is the third-largest health killer after heart disease and cancer. And according to current estimates, annual direct and indirect medical expenditures for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in the United States amount to as much as $50 billion. Coronary artery calcification integration algorithm Zebra's coronary calcification integration algorithm automatically calculates coronary calcification scores based on standard, non-contrast thoracic tomography. This tool can detect early if people have serious cardiovascular problems. Coronary calcification scores are biomarkers of coronary artery disease and a powerful indicator of cardiovascular disease such as heart disease or stroke. The traditional coronary calcification score must be evaluated by special angiography or non-contrast, cardiac-controlled cardiac tomography. Recently, there has been a fairly reliable derivation of coronary calcification scores, which was obtained by low-dose thoracic tomography. In addition, Zebra is constantly developing new algorithms, hoping to predict disease occurrence from common radiographic (X-ray), mammography, head computer tomography, nuclear magnetic resonance and other image data. Such as detecting malignant breast lesions, detecting acute cerebral hemorrhage, measuring the risk of pulmonary hypertension, measuring the risk of aortic aneurysm, detecting chest X-rays, detecting lung nodules from chest tomography. Partner Zebra's automated algorithms and clinical insight decision support tools attract more than 1,100 hospitals and healthcare facilities and form a network of partners, including Keystream, Intermountain Healthcare, University of Virgina health system, Clalit, Cedars-Sinai, Mahajan Imaging, Teleradiology soluTIons, NTTDATA, RIMA, HenryFord health system, Nuance, University of Oxford, Assistance Hopitaux Publique, Google Cloud Platform, etc. Financing situation Zebra currently has two rounds of financing of $20 million. On April 6, 2015, they received 8 million investments from Khosla Ventures, Marc Benioff, and Deep Fork Capital. On May 24, 2016, the company received $12 million in investments from Intermountain Healthcare, Khosla Ventures, Dolby Family Ventures, Marc Benioff, and OurCrowd. Awards From 2014 to the present, in just three years, Zebra has accumulated “the world's largest anonymous database of medical imaging and clinical data†and even surpassed IBM. Such a fast-rising company has won many honors. Ranked as one of the top 5 artificial intelligence companies in the world by FastCompany magazine, and was named the top 50 artificial intelligence leader by Fortune magazine, and was named Cool Codor by Gartner and selected by Frost & Sullivan. For the 2017 technology innovator, he was awarded the Ayn Rand Foundation's Social Impact Award.
Semiconductor Stud Devices are mainly used for rectifying and switching
By using the unidirectional conductivity of the diode, alternating direction alternating current can be transformed into pulse direct current in a single direction.
Applications for Medium power switching and DC power supplies.
Semiconductor Stud Devices,Stud Mounted Semiconductor Devices,Stud Mounted Power Semiconductor Device,Ir Semiconductor Stud Thyristor YANGZHOU POSITIONING TECH CO., LTD. , https://www.pst-thyristor.com