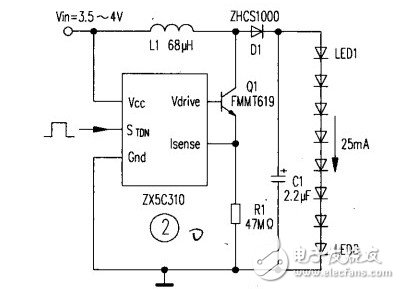
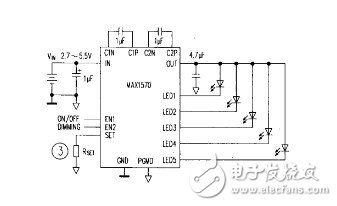
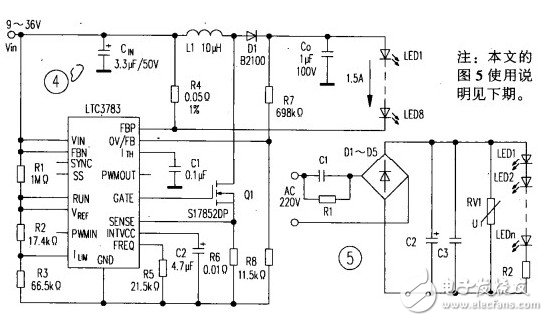
With the birth of white LEDs and their rapid development, LEDs began to enter the general lighting stage. LED is a solid-state cold light source, the fourth generation of electric light source after the incandescent, fluorescent and high-intensity discharge lamps (HID). It is now widely used in the fields of building lighting, street lighting, landscape lighting, signage, signal lights, and lighting in residential buildings. There are currently three main types of LED-powered power supplies: low-voltage batteries, solar cells, and AC mains. Regardless of which raw power source is used, it must be converted to meet the operating conditions of the LED. Such a power conversion circuit generally refers to an LED driving circuit. In LED solar power systems, batteries or supercapacitors are also needed to store solar energy. When lighting is required at night, the battery or supercapacitor is discharged through the control circuit to supply power to the LED drive circuit. The combination of solar and wind energy and LED is a highlight of LED applications. It will bring light to the poor and remote areas of the Third World, and let the brilliance of green lighting illuminate every corner of the world. 1. When the input voltage is higher than the LED voltage When the input voltage is higher than the voltage drop of the LED or LED string, a linear regulator or a switching buck regulator is usually used. (1) Linear regulator The linear regulator is a DC-DC buck converter. Most of the linear regulators used in the LED driver circuit are low-dropout regulators (LDOs), which have the advantage of not requiring inductive components, requiring a small number of components, no EMI, and low voltage drop. However, compared with switching regulators, LDOs have higher power losses and lower efficiency. LDOs often need to add a heat sink when driving high-power LED strings of 350mA or more. (2) Switch type buck regulator A switching buck regulator based on a monolithic dedicated IC requires an inductive component. Many buck regulators have switching frequencies above 1MHz, resulting in very small external components, occupying very small space and achieving efficiencies of over 90%. However, such converters generate switching noise and have EMI problems. Figure 1 shows a 3W LED step-down driver circuit based on the Zetex ZXSC300. The RCS is a current sensing resistor, and D1 is a 1A Schottky diode. At an input voltage of 6V, the current through the LED is 1.11A. The ZXSC300 is available in a 5-lead SOT23 package. There are many buck converter monolithic ICs that integrate the switching MOSFET (Q1) and the buck diode (D1) on the same chip, further reducing the number of external components. 2. When the input voltage is lower than the LED voltage When the input voltage is lower than the total forward voltage drop of the LED or LED string, the LED requires a boost drive circuit. There are two main types of boost converters. (1) Inductive boost converter In mobile phone backlighting, an inductive step-up LED driver circuit is often used. A switched inductor boost converter is used to drive a string of LEDs consisting of one or more LEDs with equal current through each LED. If one LED is open in the LED string, the other LEDs will go out. Figure 2 shows the inductor-boost LED driver circuit. The LED string consists of eight NSPW500BS white LEDs from Nichia Chemical Co., and the current through each LED is about 25mA at an input voltage of 4V. At present, most of the boost regulator ICs integrate the switching transistors in the chip, and some also integrate Schottky diodes. (2) Switched capacitor (charge pump) boost converter The switched capacitor boost converter is also a charge pump. The charge pump dedicated IC has a built-in switch, and is connected to one or two 1μF charge and discharge capacitors. The charge pump mode of operation is 1 & TImes;, 1.5 & TImes; and 2 & TImes;, in recent years there have been 1.33 & TImes; (4 / 3 times) and 4 × mode. When the output voltage is close to the input voltage, the charge pump does not need to be boosted, ie, operates in 1X mode. When boost is required, switch to 1.5x or other operating mode. The charge pump circuit can drive the LED array or drive only one LED. Figure 3 shows the MAX1570-based charge pump driving five white LEDs. The MAX1570 is available in a 4mm x 4mm 16-pin QFN package with a maximum thickness of 0.8mm. The MAX1570 has an input voltage range of 2.7V to 5.5V, operates at a fixed frequency of 1MHz and operates efficiently in 1x and 1.5x modes, providing 30mA for LEDs. Constant current, LED current matching accuracy of 0.3%, and LED current can be set by a single resistor RsEr. LED brightness can be controlled via digital input or PWM, consuming only 0.1μA in the off state. 3. When the input voltage may be higher or lower than the LED voltage A buck/boost converter must be used when the input voltage can be higher or lower than the total voltage drop of the LED or LED string. A circuit based on the LT°C3783 buck/boost converter drives eight 1.5A series LEDs as shown in Figure 4. The input voltage range of the LED string driving circuit is 9~36V, and the total voltage drop of the LED string is 18~37V. Under the condition of VIN=14.4V, Vo=36V and I0=1.5A, the output power is 54W, and the efficiency is up to 93%. The switching frequency of the circuit is determined by the IC pin FREQ Resistor R5 is set (frequency range is 20kHz~1MHz). The voltage divider composed of R7 and R8 sets the output overvoltage protection level. R4 is connected between IC pin FBP and the high side line to sense the LED current. The LTC3783 supports multiple topologies. It can also be used to construct circuits such as boost converters and buck converters. Flyback converters, single-ended primary inductor converters (SEPIC), and CUK regulators can all increase or decrease the input voltage. The output and input voltage can be the same or opposite in polarity. Each topology has unique advantages, but is less efficient than a buck-boost regulator. The utility model provides a disposable electronic cigarette, comprising: a hollow shell, the bottom of the shell is provided with a lower cover; the shell contains an atomizer, and the outer side of the atomizer is sheathed with a disposable cigarette A bomb, a microphone cover is arranged under the atomizer, a microphone is covered under the microphone cover, a battery is arranged on one side of the atomizer, and an upper cover is arranged on the top of the casing; The atomizer includes an atomizing core, an oil-absorbing cotton sleeved on the outside of the atomizing core, and an atomizer outer tube sleeved on the outside of the oil-absorbing cotton. The disposable electronic cigarette provided by the utility model absorbs the smoke oil on the surface through the absorbing cotton, and then atomizes the smoke through the atomizing core, which greatly reduces the risk of oil leakage, at the same time, reduces the burning of cotton and ensures the smoking taste.The utility model provides a disposable electronic cigarette, comprising: a hollow shell, the bottom of the shell is provided with a lower cover; the shell contains an atomizer, and the outer side of the atomizer is sheathed with a disposable cigarette A bomb, a microphone cover is arranged under the atomizer, a microphone is covered under the microphone cover, a battery is arranged on one side of the atomizer, and an upper cover is arranged on the top of the casing; The atomizer includes an atomizing core, an oil-absorbing cotton sleeved on the outside of the atomizing core, and an atomizer outer tube sleeved on the outside of the oil-absorbing cotton. The disposable electronic cigarette provided by the utility model absorbs the smoke oil on the surface through the absorbing cotton, and then atomizes the smoke through the atomizing core, which greatly reduces the risk of oil leakage, at the same time, reduces the burning of cotton and ensures the smoking taste.The utility model provides a disposable electronic cigarette, comprising: a hollow shell, the bottom of the shell is provided with a lower cover; the shell contains an atomizer, and the outer side of the atomizer is sheathed with a disposable cigarette A bomb, a microphone cover is arranged under the atomizer, a microphone is covered under the microphone cover, a battery is arranged on one side of the atomizer, and an upper cover is arranged on the top of the casing; The atomizer includes an atomizing core, an oil-absorbing cotton sleeved on the outside of the atomizing core, and an atomizer outer tube sleeved on the outside of the oil-absorbing cotton. The disposable electronic cigarette provided by the utility model absorbs the smoke oil on the surface through the absorbing cotton, and then atomizes the smoke through the atomizing core, which greatly reduces the risk of oil leakage, at the same time, reduces the burning of cotton and ensures the smoking taste. maskking vape,maskking vape price,maskking vape review,maskking vape shop,,maskking vape cost,maskking vape disposable,maskking vape informacion Suizhou simi intelligent technology development co., LTD , https://www.msmvape.com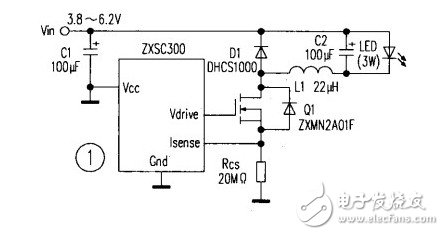
Detailed description of the basic design of the LED power drive circuit
LED power drive circuit analysis