In the automatic control system, P, I, D adjustments are proportional adjustment, integral adjustment, and differential adjustment. Adjusting the quality of control depends on the reasonable selection of control law and the setting of parameters. It is always desirable in the control system that the controlled parameter is stable within the process requirements. However, in practice, the controlled parameter always has a certain difference from the set value. The principle of selection of regulation rules is: effective regulation laws can quickly overcome interference. Proportional-integral control is proportional to timely addition of integrals to eliminate bias. Integral will slow down the control and will degrade system stability. Proportional integration is suitable for large object lags and large changes in load, but the rate of change is slow and requires no residuals in the control results. Widely used in flow, pressure, liquid level, and those without specific time lag. In the automatic adjustment system, E=SP-PV. Among them, E is the deviation, SP is the given value, PV is the measured value. When the SP is greater than PV, it is a positive deviation, and vice versa is a negative deviation. The action of the proportional adjustment action is proportional to the magnitude of the deviation; when the proportionality is 100, the proportional action output and deviation are 1:1 action of the respective range range. When the ratio is 10, press lO: l action. That is, the smaller the degree of proportionality. The stronger the proportional effect. A too strong proportional effect can cause oscillations. Too weak results in an underbalanced proportion, resulting in too many fluctuation cycles in the system's convergence process and a low attenuation ratio. Its role is to stabilize the adjusted parameters. The action of the integral adjustment action is proportional to the integration of the deviation over time. That is, there will be an output if the deviation has an integral action. It plays a role in eliminating residuals. A too strong integral action can also cause oscillations. Too weak will cause a residual error in the system. two PID control (in fact there are only used PI and PD control), is based on the system error or system error rate of change, the use of proportional, integral, differential calculation of the control amount to control. The goal of any closed-loop control system's regulation is to make the system's response to a fast (fast), quasi (accurate), stable (stable) optimal state. The main task of PID adjustment is how to achieve this goal. Increasing the proportional P term will speed up the response of the system. Its role is to amplify the magnitude of the error. It can quickly affect the control output value of the system, but the system cannot be well stabilized at an ideal value only by the effect of the proportional coefficient. The result is that although the effects of disturbances are more effectively overcome, steady-state errors occur. Excessively large scale factors also cause the system to overshoot and produce oscillations, which degrades stability. The role of the integral I term is to eliminate the steady-state error. It can perform error correction on the system with accumulated error after stabilization and reduce the steady-state error. In integral control, the output of the controller is proportional to the integral of the input error signal. three There are many ways to adjust the PID controller parameters. There are two general categories: Smart Sensor,PIR Motion Sensor,Door Sensor Chinasky Electronics Co., Ltd. , https://www.chinacctvproducts.com
The relationship between proportional, integral, differential and matching use effect
The proportional adjustment is simple, the control is timely, the parameter setting is convenient, and the control result has a residual error. Therefore, the proportional control law adapts to the object capacity, the large load change is not large, the pure lag is small, and a system with a residual error is allowed, which can generally be used for the control of the liquid level and the secondary pressure.
Proportional differential control: fast response, small deviation, can increase system stability, have advanced control, can overcome the inertia of the object, and control results have residual error. Adapt to the object lag, load change, the controlled object changes infrequently, the result allows a system with residual.
The differential adjustment action is proportional to the rate of change of the deviation. The effect is to prevent all changes in the parameters being adjusted and to have the effect of advance adjustment. It has a good effect on large lagging objects. However, pure lag cannot be overcome. Suitable for temperature regulation. Using differential adjustment can shorten the system's convergence cycle time. A long derivative time can also cause oscillations. The method of parameter setting is generally performed in the order of differentiation after the first integral. Look at the curve adjustment parameters and gradually find the best parameters from the curve of the adjustment quality. In the follow-up system, the use of digital PI control can achieve high control accuracy, no overshoot, fast response, high curve fitting accuracy, and simplifies the control circuit. The traditional positional PI algorithm can generally meet the basic control requirements, but there must be a premise: the control period should be small enough. If the control period is too long and the curve fit is poor, it may be difficult to achieve a curve fitting error of 15%. It may even cause the system to lose control and cause damage to the mechanical equipment.
Therefore, for the control system mentioned in this article, the location-based PI algorithm cannot be used simply, but it should be improved to meet the requirements of the control system. The proportional coefficient K is directly related to the deviation of each sampling. Therefore, increasing the Kp can make the system respond faster; meanwhile, the integral coefficient IX tail is related to all the previous sampling bias values. Due to the long sampling period, the error of each sampling is affected. Larger, so reducing the integral coefficient is good for improving the control accuracy. However, increasing the proportional coefficient and reducing the integral coefficient will cause the computer to change the output value each time. 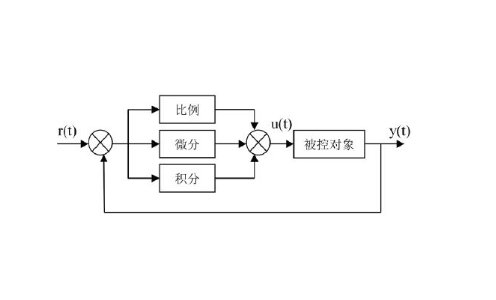
For an automatic control system, if there is a steady-state error after entering the steady state, the control system is called a poor system. In order to eliminate the steady-state error, an integral term must be introduced in the controller. The effect of the integral term on the error depends on the time integral. As time increases, the integral term increases. In this way, even if the error is small, the integral term will increase with time, which will push the output of the controller toward the steady-state error reduction until the steady-state error is equal to zero. Differentiating has a leading role. For a control system with hysteresis, differential control is introduced. When the differential term is set properly, it has a significant effect on improving the dynamic performance of the system. It can reduce the overshoot of the system and increase the stability. The dynamic error decreases. In differential control, the output of the controller is proportional to the derivative of the input error signal (ie, the rate of change of the error). The automatic control system may oscillate or even lose stability during the process of overcoming the error adjustment. The reason is that there is a controlled object with a large inertial link or lag, which has the effect of suppressing errors, and the change always lags behind the change of error. . The solution is to "advance" the change in the effect of suppressing errors, that is, when the error is close to zero, the effect of suppressing errors should be zero. The differential term can predict the trend of error change, so that the control action of the suppression error is made to be equal to zero or even negative in advance, thereby avoiding the serious overshoot of the controlled amount and improving the dynamic characteristics of the system in the adjustment process.
The first is the theoretical calculation method. It is mainly based on the mathematical model of the system. After the theoretical calculation, the controller parameters are determined. This method may cause the PID parameters obtained due to the inaccuracy of the system model cannot be directly applied, and must also pass the engineering. Actual adjustments and modifications;
The second is the engineering method. It mainly relies on engineering experience and is carried out directly in the test of the control system. This method is simple, easy to master, and widely used in engineering practice. In engineering practice, the adjustment methods of PID controller parameters mainly include critical ratio method, reaction curve method and attenuation method. Each of the three methods has its own characteristics, and all of them have the common point that they pass the test, and then adjust the controller parameters according to the engineering experience formula. However, no matter which method is adopted, the controller parameters need to be adjusted and improved in the actual operation.
Now generally used is the critical ratio method, using this method to adjust the PID controller parameters are as follows:
1 First select a short enough sampling period for the system to work;
2 Only add the proportional control link until the system shows a critical oscillation for the input step response, and note the proportional amplification factor and the critical oscillation period at this time;
3 Calculate the parameters of the PID controller through a formula under a certain degree of control. Debugging example of PID controller parameters After the basic parameters of the speed control system are set, the next step is to adjust the PID parameters to achieve the best control effect.
In the following, the PID regulator of a diesel engine power plant with a control target at a constant speed is taken as an example to specifically describe the adjustment procedure of the engineering method.
(1) Proportional parameter: The maximum proportional gain should be used when the rotational speed is stable. Increase the proportional gain until the speed starts to fluctuate, then reduce the proportional gain until the ripple stops. If there has been no rotational speed fluctuation, the actuator linkage is dithered and then the proportional gain is reduced until the fluctuation stops. However, if the proportional gain is too large, the system speed will oscillate. In this case, the proportional gain should be reduced.
(2) Integral parameters: The maximum integral gain should be used while keeping the rotational speed stable. Increase the integral gain until the speed starts to fluctuate, then reduce the integral gain until the ripple stops. If there is no rotational speed fluctuation, the actuator linkage is dithered and then the integral gain is reduced until the fluctuation stops. However, if the integral gain is too large, the system speed will oscillate. In this case, the integral gain should be reduced.
(3) Derivative parameters: Increase the derivative gain until the reaction appears to have minimal overshoot of load transients. However, if the differential gain is too high, the system speed will oscillate. In this case, the differential gain should be reduced.
(4) PID adjustment sequence: When debugging, you can adjust the proportional parameter first, then adjust the integral parameter, finally adjust the differential parameter, and then adjust the proportional parameter and integral parameter. If necessary, repeat steps (1) to (3) until the desired effect is achieved.
PID control is the most widely used regulator control law in engineering practice. It has the advantages of simple structure, good stability, reliable work and easy adjustment. However, in the actual online debugging, it is necessary to follow certain rules and master certain debugging skills in order to adjust the control system to the best effect quickly and well. The temperature control system has the characteristics of non-linear, time-varying and hysteresis, and the circulating water in the boiler water temperature control system is also a strong interference, which increases the complexity of the system control, the conventional PID control effect is not ideal, and the fuzzy PID parameter self-tuning The control algorithm can obviously improve the nonlinearity, time-varying and large-delay in the temperature system, and it also has good ability to suppress words and phrases.
Basic theory of PID control
Teaching PID parameter adjustment experimental device research The majority of automatic control devices used in the automatic control system of the current production process, although their structure is different, but they have the control law is proportional, integral and differential law (ie PID control Law), the enemy called PID controller. During the development of automatic control of the production process, the PID controller is the oldest and most vital basic control device. The PID controller has the following advantages:
(1) The principle is simple and the application is convenient.
(2) strong adaptability. Has been widely used in electric power, machinery, chemical industry, thermal industry, metallurgy, building materials and oil and other production sectors.é…ƒ is the computer control system of the process of the most salary development at present, and its basic control law is still PID control law.
(3) Robustness. That is, its control quality is insensitive to changes in the characteristics of the controlled object. When most controlled objects are disturbed by the outside world, especially when the external load changes, the dynamic characteristics of the controlled object tend to change greatly. In order to meet the required control performance, it is necessary to constantly change the parameters of the controller. It is very troublesome.
If the controller is robust, there is no need to change the controller's parameters frequently.