The opportunities and future brought by artificial intelligence to Southeast Asia
In recent years, advances in data collection and integration, algorithms, and computer processing have led scientists and engineers to make significant advances in the development of artificial intelligence (AI). Suddenly, the machine has been able to accomplish tasks that once required human cognition. In the past, computers were only able to execute fixed programs that were already written. Now, people can provide a common strategy for computer learning that enables them to process new data without having to be reprogrammed. At present, many "machine learning" systems like this have been put into commercial use. In the fields of finance, healthcare and transportation, the "machine learning" system is becoming more and more widely used. These systems have begun to have an impact in ten ASEAN countries (ASEAN, English name ASEAN).

The two major global centers for artificial intelligence development are the United States and China. The United States has taken the lead in developing many applications, and China is still in second place, but its development momentum is rapid. In contrast, ASEAN countries are lagging behind, but each of them has some progress in artificial intelligence. Among them, Singapore has the most research results, and in Malaysia and Vietnam, it is very encouraging to see some early results. Although artificial intelligence tools are being adopted in industries such as transportation, financial services, healthcare, and media, the technology industry is still at the forefront of development.
Because artificial intelligence technology can significantly increase productivity, it can have devastating effects on the economy of Southeast Asia and the workers there. Previously published MGI research estimates that existing artificial intelligence technologies are likely to automate half of the existing work activities of the four ASEAN economies: Indonesia (52%), Malaysia (51%), the Philippines (48%) and Thailand ( 55%). These jobs currently generate more than $900 billion in wages.
However, it is worth noting that technical feasibility is not the only factor that affects job automation. Companies will also consider factors such as cost of purchasing and implementing technology, labor market dynamics, business interests, regulation, and social recognition. But it seems that the nature of many existing jobs will change, and more and more jobs need to interact with machines, for which Southeast Asia will need to develop new types of workforce skills.
If AI technology is used in the right way, it is likely to have a positive social impact for ASEAN countries. For example, machine learning innovation can improve credit models and enhance financial inclusion. Artificial intelligence solutions can provide new types of preventive and telemedicine, assist in disease diagnosis, and accelerate the development of new drugs. Adaptive learning algorithms can play a role in virtual education and personalized teaching. To achieve these uses, most parts of Southeast Asia will need to establish basic digital facilities and data ecosystems.
For most ASEAN companies, they will need to make fundamental changes to their management culture, including data-driven decision making; the most important of these is to build innovative partnerships with professional companies to incubate artificial intelligence. Scarce skills required in the field. In addition, companies need to prioritize funding and manpower to develop effective ways to strengthen data infrastructure.
Although the market will become a driving force for the development and popularization of artificial intelligence, the government still needs to play a key role in bringing benefits to society as a whole. In summary, there are three key points: establishing a regional policy framework to support the development and popularization of artificial intelligence; developing artificial intelligence talents and encouraging use at the local level; focusing public opinion on artificial intelligence to achieve inclusive growth, Bring positive social impact.
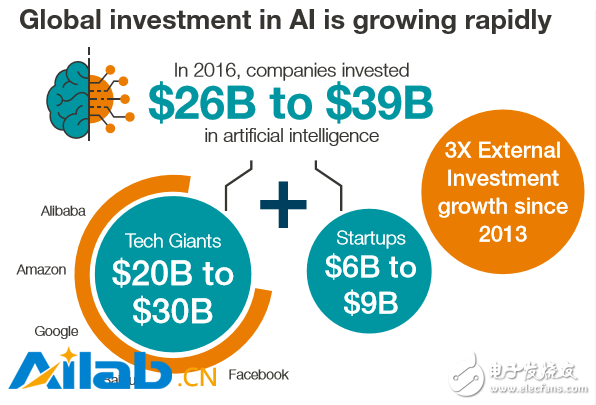
Figure: Artificial intelligence global investment is growing rapidly
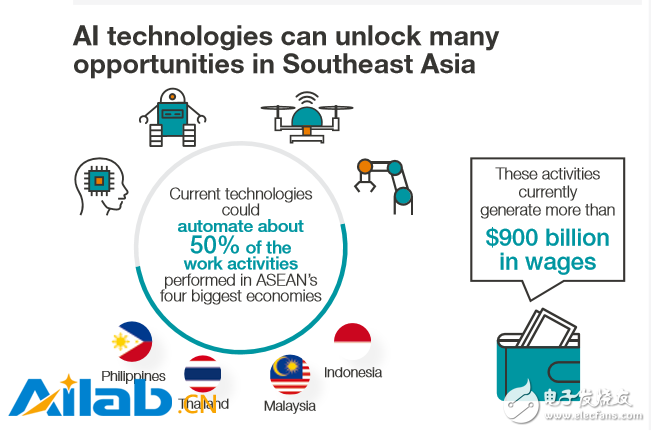
Figure: Artificial intelligence technology brings many opportunities to Southeast Asia
The potential social benefits of artificial intelligence technology after large-scale application: The first is that machine learning innovation can improve the credit model and enhance financial inclusiveness; the second is that artificial intelligence solutions can provide new preventive medical and telemedicine, and assist Disease diagnosis can also speed up the development of new drugs; thirdly, adaptive learning algorithms can play a role in virtual education and personalized teaching.
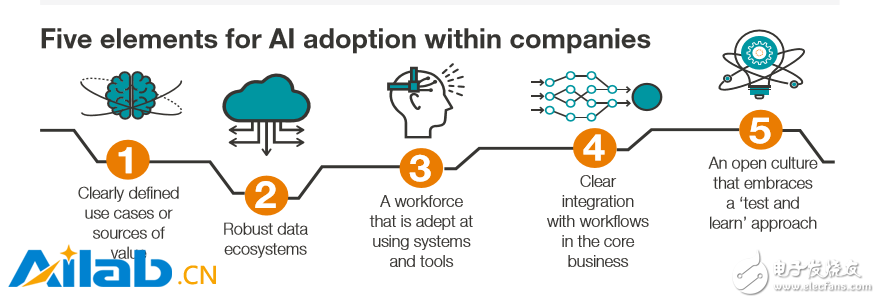
Figure: Five basic elements of using artificial intelligence within the company
I. Prospects for the future of artificial intelligenceArtificial intelligence (AI) refers to the ability of machines to display human intelligence. For example, the ability to solve problems without the need for detailed, manually developed software assistance. By consulting a large number of pattern datasets, machines can "learn" to perform tasks such as identifying images, recognizing speech, identifying relevant information in text, integrating information, drawing conclusions, and making predictions. With the rapid development of artificial intelligence technology, its practicality has also been improved in more and more fields.
There is no universally consistent definition of the composition of artificial intelligence. This area is currently evolving rapidly, and developers often combine existing technologies to solve specific problems. Therefore, the term "artificial intelligence" covers a wide range of technologies and applications, some of which are extensions of earlier technologies (such as machine learning), and others are other entirely new technologies. In fact, there is no “smart†theory that is generally accepted, and the definition of artificial intelligence is constantly changing as people's understanding of current progress. Although there is disagreement about how to define boundaries in this area, one thing is widely shared: artificial intelligence will bring the next wave of digital subversion.
Artificial intelligence and the employment opportunities it brings
People are increasingly aware of (and anxious about) that artificial intelligence can have devastating effects on the labor market. The previously released MGI research project shows that almost half of the current work activities are automated, which can be achieved by adapting existing technologies. Currently, 30% of activities in 60% of occupations can be achieved through automated technology (see Figure 1). Since automated applications are at the task level, artificial intelligence seems to change more and more occupations, but it will not be completely eliminated. This may have a profound impact on the demand for certain workforce skills in Southeast Asia and may exacerbate labor market turmoil.
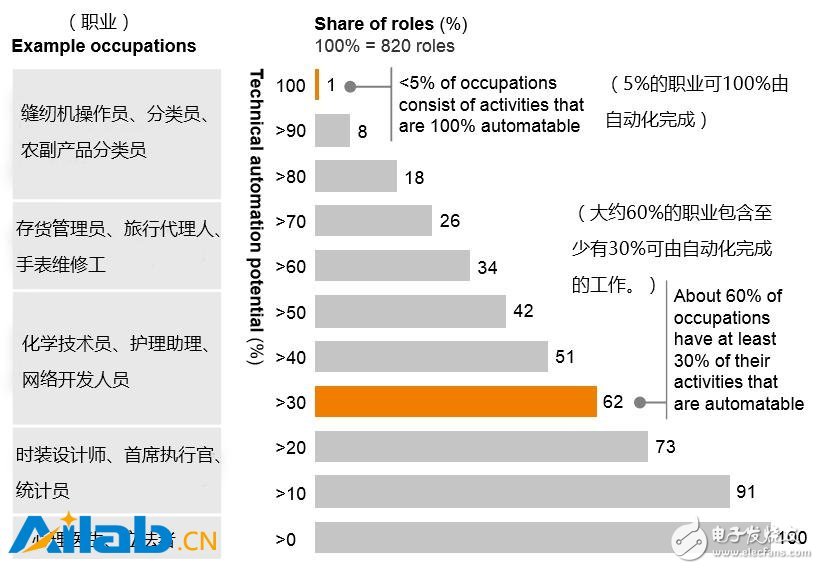
Exhibit 1: Although there are few occupations that can be fully automated, 60% of current occupations include at least 30% of activities that can be done through automated technology. 5% of occupations can be 100% automated, and approximately 60% of occupations include at least 30% of work that can be done automatically.
Occupations that contain a large amount of data collection, processing, or fixed procedures in their work will be affected first. These occupations include food processing, office management and factory production. This impact on the labor market can be enormous. In Southeast Asia, MGI found that existing technologies can automate more than half of the work activities in Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines and Thailand, with 52%, 51%, 48% and 55% respectively. These jobs currently generate more than $900 billion in wages. But this does not mean that, just because it is technically feasible, companies will replace workers with machines overnight. The speed and scope of enterprise automation will depend on how they view business cases, weigh the cost and ease of use of these technology systems, labor market dynamics, possible value creation, customer experience, capabilities, regulation, and social acceptance.
Artificial intelligence has the potential to dramatically increase productivity due to technology disruptions that have occurred in the past, and productivity has always been the key to generating revenue growth and promoting economic prosperity. According to MGI estimates, assuming that the replaced human workforce can be redeployed to jobs that are still as efficient as in 2014, the spread of artificial intelligence will increase global GDP by 0.8% to 1.4% annually. But this opportunity not only increases efficiency today, it also creates new avenues for future growth. In our survey of “artificial intelligence†executives, 20% of them used labor cost savings as their primary motivation for artificial intelligence. But more people (25%) said they introduced artificial intelligence to expand their business.
Artificial intelligence technology is approaching a tipping point
People's expectations for artificial intelligence are soaring. As costs fall, the computing power of computers is growing exponentially, enabling companies and organizations to run complex algorithms on large data sets. Today, algorithms that operate on large data sets have transcended human capabilities in areas such as image and speech recognition. Perhaps most importantly, with the spread of mobile devices, a large amount of new data is being generated that reflects all aspects of the consumer's lifestyle and how it is consumed. In fact, the world generates about 2.2 EB (2.2 billion GB) of new data every day. These trends have led to significant advances in the field of artificial intelligence – and these advances have moved out of the laboratory into real business applications (see Exhibit 2).
Machine learning is the basis of most current artificial intelligence use cases. It is based on algorithms that update by identifying patterns in large data sets without the need for rule-based programming to operate or draw conclusions. In practice, machine learning can be used to study project outcomes such as consumer demand or public health needs. It also optimizes equipment maintenance, adjusts prices, adjusts marketing information, and delivers a personalized retail experience.
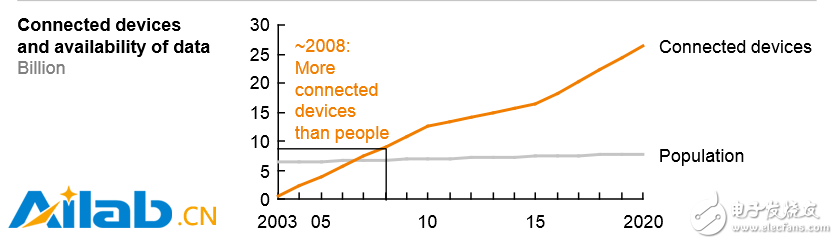
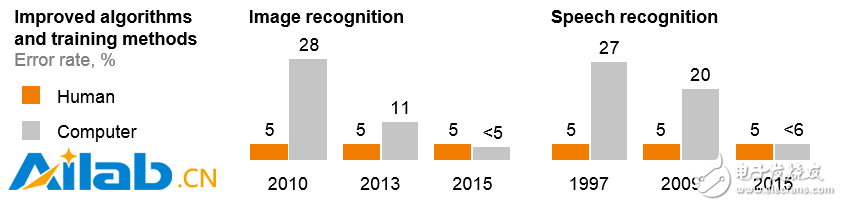
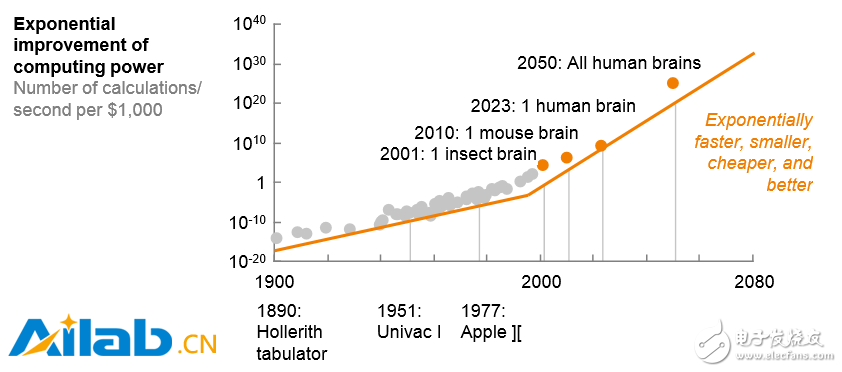
Figure 2: Due to the emergence of various favorable conditions, the popularity of artificial intelligence is reaching a critical point. Connected devices and data availability (in billions), improved algorithms and training methods (error rate, %).
In addition: combined with information processing (such as computer vision and natural language) and drive technology (robots and autonomous vehicles), machine learning technology has the potential to change many aspects of our daily lives (see Figure 3).

Exhibit 3: Artificial intelligence will change our daily habits to improve quality of life and human productivity.
TuTI is a mother whose daughter is Andira. She is also a middle manager of a green energy company based in Jakarta.
(1) In the morning, her virtual assistant helped her to preview the plan for the day, including: the doctor gave her a health reminder. Confirm the order for the groceries to be delivered that evening. Andira's school sent notifications about homework and how TuTI interacted with her based on machine learning.
(2) TuTI and Andira read together on the road to the school by driverless car, which is safer, smoother and faster than driving, thanks to intelligent route planning and traffic monitoring.
(3) At the company, TuTI is the chief engineer of a wind farm. Her virtual assistant provided her with the latest information in this field. It helps Tuti sort out the tasks that need to be prioritized that day, because it already knows when and how Tuti works most efficiently. The system's output mode is abnormal, drawing her attention to one of the generators; but the robot can remotely inspect and repair it, minimizing production loss and safety hazards.
(4) After work, Tuti went to the gym for a quick workout. The virtual assistant refers to Tuti's health notice and proposes changes to her workout schedule.
(5) Back home, Tuti helps Andira to complete homework, and there is a virtual tutor next to it. The tutor's content comes from a virtual teacher who also collects data during the process of guiding Andira and incorporates it into an anonymous country. Level database to improve the overall quality of teaching in Indonesia.
Although the pace of change is uncertain, the changes are indeed happening and have begun to penetrate traditional non-technical industries such as manufacturing. For example, Foxconn deployed 40,000 robots in its Chinese factories, making the factory less labor intensive. In fact, Foxconn is still planning further, with the goal of producing 10,000 robots within the company to achieve its industrial automation goals.
Declining costs, modularity of technology components, and the development of user-friendly tools and interfaces are rapidly making artificial intelligence a viable and necessary operational asset for more and more companies. They can now connect off-the-shelf data management platforms to their most important assets to get the lowest upfront costs.
Early adopters of artificial intelligence will take advantage
As the early wave of digital technologies showed, early adopters of artificial intelligence can take a major competitive advantage and continue to maintain this advantage over time—especially if they see this new technology as a Key business capabilities and future sources of revenue growth, not just a means of cutting costs. Big companies do better in this area because they have the ability to invest in early trials and achieve greater return on investment by gradually expanding the scale of their business.
Our estimates show that in 2016, companies worldwide invested between $20 billion and $30 billion in artificial intelligence. This includes both internal R&D investment and stable acquisition flows. So far, technology giants such as Alibaba, Amazon, Baidu, Facebook and Google have invested more than three-quarters of their total investment in artificial intelligence. From 2011 to February 2017, these companies completed 29 of the 55 large M&A transactions in the US and 9 of the 10 major transactions in China.
Active investments are helping these companies gain access to key talent, technology and data sets, potentially creating barriers for their chronic competitors. Early adopters of artificial intelligence were able to use artificial intelligence as a unique advantage to enter the relevant industries. Artificial intelligence assistants like Siri, Alexa, or Cortana can serve applications in new areas such as healthcare and implement functions such as recommending hospitals or experts based on a person's unique medical history, or monitoring chronic disease indicators in real time. The realization of these possibilities will make the long-standing industry boundaries increasingly blurred.
Native digital companies also have their unique advantages. They understand the value of the vast amount of clean data that they get from their core business. They usually use agile "test and learn" methods in their operations. They have a clear understanding of how artificial intelligence technology can enhance its core business, whether it's Amazon's Kiva robot or Facebook's personalized robot. Existing traditional industry companies can adopt their technology, but will find it difficult to catch up with them.
In ASEAN, industry players in the high-tech industry (banking and telecommunications) who are most proficient in digital technology have begun to take action, but they are shorting. Many of ASEAN's telecom operators have begun to enter the field of artificial intelligence to optimize customer intelligence, but they have encountered difficulties in expanding their business, often because of their lack of key skills in data science and business translation. In the absence of bold interventions, participants in other industries are likely to encounter the same obstacles, forcing them to rely on professional technology providers. Perhaps the most striking example is IBM's Watson system (see Item 1).
Source 1: IBM Watson, the world's most famous artificial intelligence system
IBM has introduced the concept of artificial intelligence to the public through its "Watson" supercomputer. "Watson" defeated all human players in the American quiz show "Dangerous Edge". Since then, IBM has been demonstrating "Watson" cloud-based predictive analytics capabilities to customers in a variety of industries. In order to have the ability of humans to answer questions, Watson uses 80 trillion floating-point operations per second to access 90 servers with more than 200 million pages of data. It can mine text, perform complex analysis of massive unstructured data, and run the world's most powerful search engine.
Watson's basic cognitive computing technology is suitable for a wide variety of applications, including the following:
(1) Healthcare and medical research: Watson can process large amounts of patient data, look for treatment options that drug researchers may not expect, and then propose new hypotheses for further evaluation. Its processing power is being used to test patients and clinical trials, diagnose cancer and determine treatment options, manage chronic diseases, and accelerate drug development.
(2) Education: Artificial intelligence has great potential for personalized teaching to adapt to each student's learning style, and to ensure that students move to more advanced topics while mastering the current content. Watson can provide critical insights based on the demographic characteristics, strengths, and weaknesses of the students, enabling teachers to develop targeted, dynamic instructional programs.
(3) Public safety: “Watson†is deployed in the intelligent city control center to predict criminal activities and assist the public security department to allocate limited resources reasonably. It can now also assess resistance to cyber threats and take corrective action accordingly.
(4) Analysis of sports events: Analysis plays an important role in professional sports. Participants can analyze a large number of performance indicators and variables to gain competitive advantage. "Watson" was used to analyze a basketball team's game, determine the skill gap of the players, and recommend who should be signed, who should be in a specific situation
(5) Media broadcast: “Watson†has been able to automatically edit video highlights, the most recent one being in Wimbledon, which usually requires a complete content operations team to complete. With this technology, the turning points in the game can be captured immediately and automatically posted on different social media channels, resulting in a greater sensation.
Second, the opportunities and challenges that artificial intelligence (AI) brings to Southeast AsiaWorldwide, the popularity of artificial intelligence is often related to the degree of digitization. In ASEAN, the pace of digital development is accelerating. In 2011, only 6% of Asian companies mentioned the terms “big dataâ€, “advanced analysisâ€, “artificial intelligenceâ€, “machine learning†and “Internet of Things†in their annual reports. By 2016, this ratio has reached one-third, indicating that these technologies are gaining momentum and are gradually becoming strategic priorities.
We found that in all industries, early adopters of artificial intelligence achieved higher profit margins than their peers (see Exhibit 4), especially in the manufacturing, financial services, transportation, and logistics industries. In order to consolidate the market and eliminate competition, most of these companies have given this residual value to customers. This "winners" situation has further exacerbated the "digitise or die" situation in which many incumbents are located.
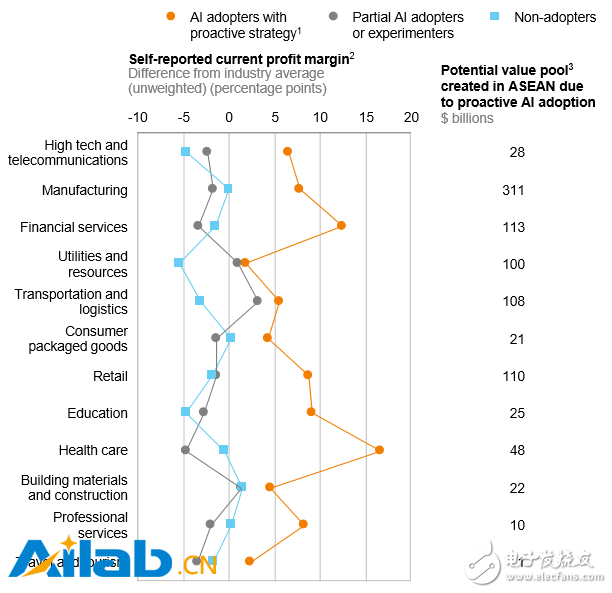
Exhibit 4: ASEAN's artificial intelligence applications create superior profitability and a huge value base
However, the adoption of artificial intelligence has not achieved its maximum value. Pre-experiment and subsequent implementation require the company to make forward-looking and extensive observations on how artificial intelligence can be applied to its core business. For companies in the traditional non-technical industry, late implementation may be prohibitive. So far, high-tech, telecommunications and financial services companies have dominated the ASEAN countries. We have also seen a surge in public service activities such as transportation and health care, driven by a number of government agencies and the Smart City program in the region.
At the national level, Singapore is a leader in artificial intelligence experiments in a variety of industries. But countries throughout the ASEAN region have some initiative (see Exhibit 5).
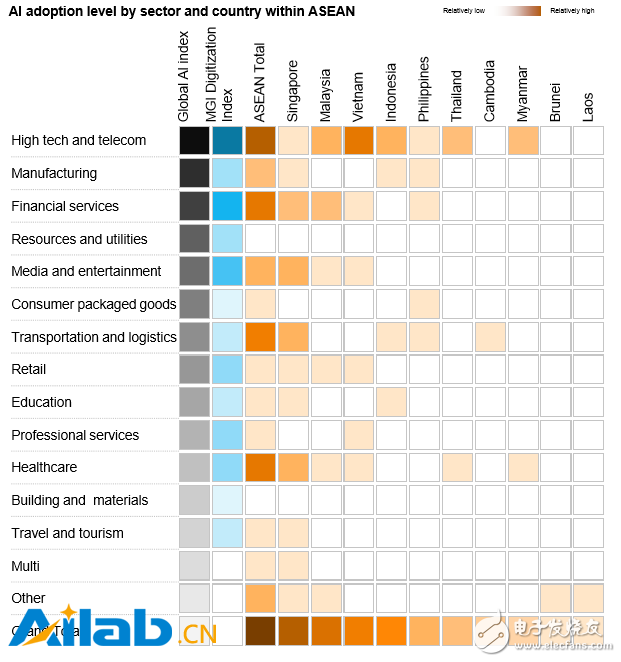
Figure 5: The popularity of artificial intelligence in various industrial sectors within ASEAN countries
While these phenomena are encouraging, ASEAN will need a clearer business case and a stronger data ecosystem. In addition, if artificial intelligence wants to realize its full potential throughout the region, it requires more harmonized talent and skills.
Development process in various areas of ASEAN
Below we will study the application of artificial intelligence in some specific industries. We start with two industries that account for about half of all ASEAN current use cases for artificial intelligence: financial, high-tech and telecommunications. After that, we focus on the manufacturing and transportation industries, which have broad development value and two priority public service areas: health care and education, all of which are likely to bring significant benefits to society.
Financial Services
So far, financial services companies in Southeast Asia have mainly improved their customer experience through artificial intelligence. For example, Hong Leong Bank of Malaysia (Malaysia) uses the IBM® Watson system to understand customer sentiment by detecting how customers speak on the phone. DBS, based in Singapore, has opened a digital bank that uses virtual assistants to predict and answer customer questions. The Hong Kong startup CompareAsiaGroup, which operates in five ASEAN countries, uses machine learning technology to connect customers with financial, communications and utility services in Asia.
For artificial intelligence, to have a broad, long-term impact on an industry, these banks in Southeast Asia may need to refer to examples of artificial intelligence that have been successfully applied in the US and China. The application of artificial intelligence to functions such as credit scoring, dynamic pricing, and digital marketing has already demonstrated its value in many places, but few companies have expanded the scale of such applications in ASEAN. To seize this opportunity, banks need to constantly develop new skills, and financial technology start-ups must continue to innovate. Of course, first of all, these companies must accelerate their basic digital pace.
Digitizing customer interactions and establishing data collection, management, and analysis processes are all priorities, because artificial intelligence tools require large amounts of data. The business case that has completed this digital transformation further reinforces the fact that ASEAN's middle-class consumers are at the heart of the consumer base, they can use digital technology, and they often shop online and choose their own satisfaction. commodity.
Almost 300 financial technology startups have invested in this area to provide solutions for online payments, p2p loans and wealth management. In theory, embedding artificial intelligence technology into their products can make them powerfully occupy the city's excellent technical strength and the ability to design practical applications for artificial intelligence, creating value for customers and making their experience Smoother, this will make the best companies stand out. The development of this field will have a huge social impact. Approximately 266 million people in the ASEAN region lack credit channels. Ultimately, artificial intelligence will provide affordable financial services to vulnerable and low-income people who are often excluded from traditional banking systems. For example, in China, Alibaba has developed the company's internal Sesame Credit Service (Zhima?Credit) using advanced analytical tools and rich business and consumer data, which may open Alibaba's way of providing loans to small loan groups. door.
Government regulators can determine the pace of innovation for financial technology companies. Over time, they may also open up the banking platform to ensure that companies compete fairly on data access. It is crucial to have carefully weighed rules between data availability and privacy, just like India's Aadhaar (Biometric Identification System). Officials may choose to allow artificial intelligence to test data in a controlled environment.
High-tech and telecommunications industry
It is not surprising that high-tech and telecommunications companies are early adopters of artificial intelligence technology. Globally, some technology giants have developed artificial intelligence applications that disrupt the traditional physical industries, such as retailers (Amazon) and entertainment (Netflix).
Its excellent results are also surprising. Amazon has saved $22 million a year after acquiring a robotics company, saving operating costs by 20%. At the same time, Netflix estimates that its artificial intelligence recommendation tool helped it avoid the $1 billion annual unsubscribe service.
Similarly, many small-scale companies in Southeast Asia are constantly working hard. Local telecommunications companies are already at the forefront because they can use their extensive population coverage and access to data, and by 2020, 90% of adults in emerging countries will use mobile subscription services.
Telecommunications companies have long used analytics tools to predict customer churn and some long-term cross-selling of additional services. But now the possibilities are much bigger – including the opportunity to enter a new type of market. People who don't have a bank account today can get basic financial services through mobile devices, and the data generated by their transactions can be used by potential customers of banks to identify insurance and other financial services such as loans. Telecom companies are also using artificial intelligence to enter other industries. . Singtel has established a data analysis subsidiary to collect, model and visualize shopper data, while India Telecom's analytics division focuses on retailers' digital marketing and bank credit scoring. ASEAN has also promoted the rise of small high-tech startups that are supported by a growing venture capital ecosystem.
By definition, the high-tech industry has intersected with all other areas involved in artificial intelligence – so terms such as financial technology, medical technology, and educational technology have also been widely disseminated. The government supports local innovators to gain certain benefits, and these innovators can pave the way for a wider spread of artificial intelligence. By improving computer science education, the government can narrow the key gaps in professional high-tech job skills, develop regulations, promote the use of anonymous data, and encourage the collection of cross-industry and cross-domain data. Singapore has taken some measures in this regard, such as encouraging entrepreneurship and providing a large amount of government grants. This move has enabled Singapore startups to succeed in the 2017 Global Entrepreneurship Ecosystem Report, ahead of Osmarks in Texas and Stockholm. In addition to establishing a startup, the government's support can also add a certain degree of visibility and prestige to domestic companies, thus retaining those who might have flowed overseas. This is also a topic we should pay attention to when discussing artificial intelligence.
manufacturing
Artificial intelligence technology will play an important role in the next phase of development in the industry. Companies will soon be able to manage the plant floor in real time and connect the entire value chain with seamless data streams for real-time decision making and increased productivity. This new world of digital manufacturing is often referred to as Industry 4.0.
In ASEAN countries, the use of artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things is a natural process. The largest companies in the region may become leaders because their business scale has already involved the areas with the greatest potential benefits. Thai food and beverage group ThaiBev and Malaysian car manufacturer Proton are just two of the major brands that aim to bring Industry 4.0 technology to their factories.
Source 2: ASEAN's Artificial Intelligence Technology Startup
In 2016, the region's total venture capital reached $2.6 billion, an increase of about 60% over the previous year. In addition, the lag in economic development and increasing social problems provide opportunities for the development of technology-driven solutions.
Many tech entrepreneurs are developing artificial intelligence technologies and applying them to local instances. These regional startups do not have the resources or talent pool that international technology giants like, but they also illustrate the importance of finding market opportunities and designing local business models in the local area.
Examples of artificial intelligence based technologies used by ASEAN startups are as follows:
Natural language processing
(1) Myanmar's Bindez uses natural language processing and text analysis to track hate speech on the Internet.
(2) Indonesia's Kata.ai is developing a Malay language processing algorithm, Malay is the main language of more than 250 million people in Indonesia and Malaysia.
(3) In Vietnam, FPT designed an artificial intelligence platform to help application developers automatically interact with end users based on natural language processing interfaces. Potential applications for such platforms include call center chat bots, virtual agents, and related voice applications.
Machine learning
(1) Network security startup Cloudsek is committed to providing machine learning-based solutions that help companies identify and address cyber threats in real time.
(2) In Indonesia, Ruangguru is exploring ways to implement personalized education services through machine learning, using the vast amount of academic data it has.
Image Identification
(1) Sero, a Vietnamese agricultural startup, provides crop intelligence to farmers through artificial intelligence analysis of images and field data.
Source 3: What is Industry 4.0?
“Industry 4.0†is a term used to describe the digital transformation of manufacturing, with the aim of combining a range of new technologies with manufacturing. The Internet of Things, artificial intelligence, robotics, and 3D printing technology can turn a factory floor into a flexible, self-maintaining operating system. Sensors can stream continuous real-time data streams into machine learning algorithms that remotely adjust complex systems, processes, and machines. These same types of systems can be used to coordinate the entire supply chain and monitor customer usage to inform future product designs and new services.
According to several studies, McKinsey estimates that Industry 4.0 can increase production efficiency by 15% to 20% in manufacturing. Excellent global manufacturers in Germany and other places have successfully demonstrated their feasibility and commercial value.
(1) Predictive maintenance: Applying machine learning tools to data collected by IoT sensors enables manufacturers to predict equipment failures and prevent machine damage and downtime through preventive maintenance. Some companies have managed to reduce overall maintenance costs by 10%.
(2) Increase in output: Industry 4.0 technology enables manufacturers to optimize the use of raw materials and increase production. An artificial intelligence semiconductor manufacturing system reduces the scrap rate of scrap metal by 30% by connecting thousands of variables to the machine group and sub-processes.
(3) Product design and after-sales service: Smart products, such as smart cars, can feed customer experience data to the product manager. This capability opens up new ways of service and is reflected in improved product design.
But many manufacturers are still hesitant considering the up-front capital investment required for modern plants and the cost of digitizing large amounts of tangible assets. Because ASEAN's labor costs are low, companies do not always see business reasons for changing their business practices.
However, in the long run, this cost calculation may change. As the region develops and the population ages, labor costs may rise, thereby reducing the size of the available workforce. China's manufacturing wages have doubled in the past decade, and Chinese companies have begun to actively adopt robotics; in fact, they are expected to invest $59 billion in machine automation by 2020.
Policymakers in the region can encourage digital transformation of manufacturing as a top priority for productivity growth, thereby promoting economic growth across the region. For example, the Singapore government supports the launch of McKinsey's Digital Competence Center (DCC), which focuses on Industry 4.0, in Singapore. Singapore DCC has established a partnership with the advanced Advanced?Remanufacturing?and?Technology?Centre (ARTC) to introduce new technologies to manufacturing companies and help them develop new capabilities. As part of the broader economic transformation blueprint, Malaysia and Thailand also include Industry 4.0.
Transportation and logistics
Rapid urbanization is putting pressure on transportation systems in cities around the world. And to solve this problem is costly: in Asia alone, the direct cost of traffic congestion is about 2% to 5% of GDP. Most of the world's major cities are struggling to solve problems related to rapid urbanization. They plan a smart city blueprint that integrates artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things to improve network efficiency by managing the infrastructure in a “smart†way.
By 2030, most cities will adopt new automotive technologies such as car sharing, autonomous driving and electrification, although these technologies will not succeed at the same time. In the future, in the most densely populated cities, “seamless movement†may be able to be implemented in the crowd, and can be brought home from home to destination. “Seamless Movement†will rely on a combination of autonomous driving and shared vehicles, complementing smart, integrated public transport infrastructure (smart cars and buses, subways and traffic management).
Private companies can play a role in realizing this vision of seamless mobility.ä¼ ç»Ÿæ±½è½¦åˆ¶é€ å•†å’Œè°·æŒã€ç™¾åº¦ç‰é«˜ç§‘技巨头æ£æ–¥èµ„数百万美元投资自动驾驶汽车,采用防撞和路线选择优化系统,以æ高安全性和é™ä½Žç‡ƒæ–™æ¶ˆè€—。ç¦ç‰¹å·²ç»ä»Žä¸€å®¶æ±½è½¦åˆ¶é€ 商转型为一家“机动车â€ä¾›åº”商。该公å¸å·²ç»æˆç«‹äº†ä¸€ä¸ªåŸŽå¸‚è§£å†³æ–¹æ¡ˆéƒ¨é—¨ï¼Œè¯¥éƒ¨é—¨å°†åˆ©ç”¨äººå·¥æ™ºèƒ½æŠ€æœ¯æ— ç¼æ•´åˆè®¸å¤šç§»åŠ¨è®¾å¤‡ï¼Œä»Žå…¬å…±äº¤é€šåˆ°å‡ºç§Ÿè½¦å†åˆ°å…±äº«å•è½¦ã€‚
æ–°åŠ å¡æ˜¯ä¸œç›Ÿåœ¨æ‰§è¡Œå…¶â€œæ™ºèƒ½ç§»åŠ¨2030â€è®¡åˆ’时的领先者,该计划è¦æ±‚人工智能系统åšåˆ°å®žæ—¶ç®¡ç†åˆ—车ã€å…¬äº¤è½¦ã€æ±½è½¦å’Œè‡ªè¡Œè½¦äº¤é€šã€‚马æ¥è¥¿äºšçš„雪兰莪州也在推行类似的计划,以åŠå°åº¦å°¼è¥¿äºšã€è²å¾‹å®¾å’ŒæŸ¬åŸ”寨的智能城市项目也æ£åœ¨è¿›è¡Œä¸ã€‚
åˆåˆ›ç§‘技公å¸æ£åœ¨æˆä¸ºè¿™ä¸€é¢†åŸŸçš„é‡è¦ç»„æˆéƒ¨åˆ†ã€‚Yogee网销售使用了机器å¦ä¹ 技术的çµæ´»ç®¡ç†è½¯ä»¶ï¼Œå› æ¤å®ƒå˜å¾—æ›´åŠ æ™ºèƒ½ï¼Œä½¿ç”¨çš„èŒƒå›´æ›´å¹¿ã€‚åœ¨7个东盟国家è¿è¥çš„å«è½¦å¹³å°Grab,已è˜ç”¨äº†200å工程师和数æ®ç§‘å¦å®¶ï¼Œä¸“注于利用人工智能改善客户æœåŠ¡ï¼Œå¹¶è¿›ä¸€æ¥ä¼˜åŒ–å…¶å¸æœºé˜Ÿä¼ã€‚
城市政府é¢ä¸´çš„紧迫挑战是与战略行业å‚与者和科技创业公å¸å»ºç«‹åˆä½œå…³ç³»ã€‚然而,这些åˆä½œçš„æ•´åˆæ˜¯ç›¸å¯¹å¤æ‚的。当然,城市的净效益是显而易è§çš„,比如å‡å°‘æ‹¥å µå’Œæ高了安全性。但è¦è°ƒæ•´ç§äººæŠ•èµ„和公共奖励的激励机制是很有挑战性的。æ¤å¤–,大多数东盟国家都专注于自动收费站,而且对大型公共投资兴趣ä¸å¤§ã€‚尽管é¢ä¸´è¯¸å¤šæŒ‘战,但在过度拥挤的东å—亚城市ä¸æ”¹å–„生活的主è¦æ½œåŠ›ï¼Œä½¿å¾—建立高效的公ç§ä¼™ä¼´å…³ç³»å˜å¾—至关é‡è¦(我们将在最åŽä¸€ç« 回到这个è¯é¢˜)。
医疗ä¿å¥
在全çƒèŒƒå›´å†…,人工智能已ç»ä»¥å¤šç§æ–¹å¼ä¸æ–展示出改善医疗æœåŠ¡çš„潜力。深度å¦ä¹ å¯ä»¥è®©æœºå™¨æŸ¥é˜…大é‡æœ‰å…³ç–¾å¹¶æ²»ç–—和结果的数æ®ï¼Œä»Žè€Œå¿«é€Ÿæ‰¾åˆ°å¯ä»¥æ”¹å–„诊æ–方案和病人护ç†çš„è§è§£ã€‚IBM利用其人工智能支æŒçš„Watson超级计算机,让医生å¯ä»¥åœ¨å‡ 秒钟内ç›é€‰æ•°ç™¾ä¸‡é¡µçš„医å¦è¯æ®ï¼Œä»Žè€Œä¸ºæ‚£è€…设计出最优的癌症治疗方案。å¯ç©¿æˆ´æœºå™¨äººè®¾å¤‡å¯ä»¥è¿œç¨‹è¿½è¸ªç—…人的å¥åº·çŠ¶å†µï¼Œå¹¶ä¸”带有æ醒功能,å¯ä»¥å®å˜±ç—…人åŠæ—¶åƒè¯ã€‚虚拟代ç†å·²ç»åœ¨åˆ†æžæ”¾å°„å¦å’Œè‚¿ç˜¤æŠ¥å‘Šï¼Œå¹¶ä¸ºç—…人æ供建议。
MGI之å‰çš„ä¸€é¡¹ç ”ç©¶ä¼°è®¡ï¼Œåœ¨åŒ»ç–—ä¿å¥é¢†åŸŸæ‰©å¤§æ•°æ®çš„使用æ¯å¹´å¯ä»¥äº§ç”Ÿè¶…过3000亿美元的价值,其ä¸ä¸‰åˆ†ä¹‹äºŒæ¥è‡ªäºŽå°†å›½å®¶åŒ»ç–—支出å‡å°‘çš„8%。
医疗ä¿é™©æ˜¯å¦ä¸€ä¸ªæœ‰æ½œåŠ›çš„储蓄领域。从全çƒæ¥çœ‹ï¼Œæœºæ¢°åˆ¶é€ 解决方案优化了索赔处ç†ã€å‡å°‘了欺诈和改善了å¥åº·çŠ¶å†µé¢„测,这å¯èƒ½ä¼šå¸¦æ¥æ›´å¥½çš„预防ä¿å¥å’Œæ›´ä½Žçš„索赔。
在东盟,在病人护ç†é¢†åŸŸå¹¿æ³›é‡‡ç”¨äººå·¥æ™ºèƒ½çš„åšæ³•è¿˜éœ€è¦æ•°å¹´æ—¶é—´ï¼Œä½†çŽ°åœ¨å·²ç»å‡ºçŽ°äº†å‡ 个æˆåŠŸçš„例åã€‚æ–°åŠ å¡æ”¿åºœæœºæž„IHiS(集æˆå¥åº·ä¿¡æ¯ç³»ç»Ÿï¼‰æ—¨åœ¨åˆ›å»ºä¸€ä¸ªå…¨å›½æ€§çš„ä¼ä¸šåˆ†æžå¹³å°ï¼Œæ±‡é›†å’Œåˆ†æžæ¥è‡ªå¤šä¸ªåŒ»ç–—ä¿å¥ç³»ç»Ÿçš„患者数æ®ï¼Œå¹¶ç”Ÿæˆæœ‰åŠ©äºŽæ”¹å–„治疗结果的è§è§£ã€‚通过æ供在线医生咨询和å¯ç©¿æˆ´å¼ä¼ 感器引导的家åºè¯Šæ–,这å¯èƒ½ä¼šä½¿ç®¡ç†æ…¢æ€§ç—…å˜å¾—å¯è¡Œã€‚其次的好处包括尽é‡å‡å°‘事故和急诊å•ä½çš„过度拥挤,以åŠå‡å°‘病人的医疗费用。åƒHolmuskè¿™æ ·çš„åˆåˆ›å…¬å¸ä¹Ÿåœ¨ä¸ºç‰¹å®šçš„病例开å‘æ•°æ®å’Œåº”用程åºï¼Œæ¯”如糖尿玻在越å—,ViCareä¿å¥åº”用程åºåœ¨Facebook?Messenger上为病人æ供了一个èŠå¤©æœºå™¨äººï¼Œå¯ä»¥ä¸ºç—…人回ç”一些基本问题。
拥有大é‡äººå£ä½†æ²¡æœ‰è¶³å¤Ÿå¤šçš„医生和专家的国家将从这些技术ä¸èŽ·ç›Šæœ€å¤šã€‚IBM的“沃森â€ä¹Ÿè®¸å¯ä»¥åœ¨å°å°¼æä¾›æœåŠ¡ã€‚2014年,å°å°¼åªæœ‰41å放射肿瘤å¦ä¸“家,å´è¦ä¸º2.5亿人æä¾›æ²»ç–—ï¼Œè€Œä¸”è¿™ä¸ªå›½å®¶è¿™ä¸€å¹´å› ç™Œç—‡æ»äº¡è¿‘20万人。
然而,该地区没有足够的整åˆæ•°æ®æ¥æ”¯æŒå…ˆè¿›çš„分æžæŠ€æœ¯ï¼Œæ›´ä¸ç”¨è¯´äººå·¥æ™ºèƒ½äº†ã€‚医院有数æ®ï¼Œä½†é€šå¸¸æ˜¯ä»¥çº¸è´¨å½¢å¼æ¥è®°å½•çš„,想è¦å…±äº«æ¯”较困难。大多数东盟国家è¦æ±‚æ•°æ®ä¸å¯ä»¥ç•™å‡ºå›½å¤–,这就é™åˆ¶äº†å»ºç«‹åŒºåŸŸæ€§æ•°æ®åº“的机会。更é‡è¦çš„是,将病人数æ®é›†ä¸åœ¨ä¸€èµ·ï¼Œå¹¶å°†å…¶å¼€æ”¾ç»™æœºå™¨å¦ä¹ ,å³ä½¿æ˜¯ä»¥åŒ¿åçš„å½¢å¼ï¼Œæˆ–者将使用å¯ç©¿æˆ´è®¾å¤‡çš„è¦æ±‚æ†ç»‘到ä¿é™©æŠ˜æ‰£ä¸Šï¼Œä¹Ÿå¯èƒ½ä¸Žéšç§è§„范和法律ä¸ä¸€è‡´ã€‚
医院和ä¿é™©å…¬å¸å°†å†³å®šè¯å“å¦‚ä½•ä½¿ç”¨äººå·¥æ™ºèƒ½ã€‚ä½†æ˜¯ï¼Œä¸Žä¼ ç»Ÿé“¶è¡Œä¸€æ ·ï¼ŒåŒ»é™¢å’Œä¿é™©å…¬å¸åœ¨è½¬å˜ç»„织的过程ä¸ä¹Ÿé¢ä¸´ç€æŒ‘战,ä¸ä»…是通过积累数æ®ï¼Œè¿˜è¦é€šè¿‡æ高他们的数å—化能力,将技术整åˆåˆ°ä»–们的工作æµç¨‹ä¸ï¼Œä»¥æ”¹å˜ä»–们的文化。创新å¯èƒ½æ¥è‡ªæ•°å—化本土公å¸ã€‚医疗ä¿å¥å…¬å¸å¯ä»¥é€šè¿‡èµžåŠ©æœ‰å‰é€”的创业公å¸æ¥ä¸Žè¿™äº›å…¬å¸ç»“ç›Ÿã€‚æ–°åŠ å¡çš„一些公å¸å·²ç»é‡‡å–了这ç§åšæ³•ã€‚政府å¯ä»¥é€šè¿‡æ供有关数æ®å…±äº«çš„监管指导,以åŠåœ¨éœ€è¦çš„时候æ供公共投资,从而促进这一过程。
教育科技已ç»æ˜¯ä¸€ä¸ªè“¬å‹ƒå‘å±•çš„é¢†åŸŸï¼Œä¸ºäººå·¥æ™ºèƒ½æ‰Žæ ¹æ供了肥沃的土壤。与金èžç§‘æŠ€ä¸€æ ·ï¼Œæ•™è‚²ç§‘æŠ€ä¹Ÿè¿Žåˆäº†ä¸€ä¸ªå·¨å¤§çš„市场:全çƒæ•™è‚²æ”¯å‡ºå å…¨çƒGDPçš„è¿‘5%。投资者注æ„到,一家投资银行预测,到2020年,教育科技投资将增长至2500亿美元。
äººå·¥æ™ºèƒ½åœ¨è¯¾å ‚ä¸Šçš„æ½œåŠ›è®©äººå…´å¥‹ä¸å·²ã€‚例如,以人工智能为基础的智能家åºæ•™å¸ˆç³»ç»Ÿï¼ˆITS)旨在æ供大规模的一对一教å¦ã€‚这些èªæ˜Žçš„导师å¯ä»¥è¿½è¸ªæ¯ä¸ªå¦ç”Ÿçš„表现,找出å¦ç”Ÿè§‰å¾—困难的概念,并为æ¯ä¸ªäººæ‰¾å‡ºé€‚åˆè‡ªå·±çš„å¦ä¹ 方法。人工智能还å¯ä»¥å‡è½»æ•™å¸ˆçš„一些日常工作,给他们更多的时间æ¥æ•™å¦ã€‚一ä½ä¹”治亚ç†å·¥å¤§å¦çš„教授在一个å¦æœŸå†…使用了一个人工智能教å¦åŠ©ç†ï¼Œå¤„ç†æ¥è‡ªä»–在线课程的1万多个问题。人工智能助手还å¯ä»¥ä»Žäº‹æ›´æ™ºèƒ½çš„å·¥ä½œï¼Œå¦‚è¯„åˆ†å’Œè®°å½•åˆ†æ•°ï¼Œä½¿æ•™å¸ˆèƒ½å¤Ÿä¸“æ³¨äºŽæ›´æœ‰åˆ›é€ æ€§å’Œæ›´å…·é™„åŠ å€¼çš„å·¥ä½œã€‚
å…¶ä¸ä¸€äº›æŠ€æœ¯å·²ç»åœ¨ä¸œç›Ÿåœ°åŒºå¾—åˆ°é‡‡ç”¨ã€‚æ–°åŠ å¡å’Œé©¬æ¥è¥¿äºšçš„大å¦å·²ç»è¯•éªŒäº†é¢„测软件,以指导能够防æ¢è¾å¦çš„干预措施。但是,东盟还有很长的一段路è¦èµ°ï¼Œæ‰èƒ½å¯¹å…¶äº§ç”Ÿé‡å¤§å½±å“。大多数æˆå‘˜å›½éƒ½æ²¡æœ‰æ”¶é›†èƒ½è®©äººå·¥æ™ºèƒ½ç®—法得出结论并åšå‡ºé¢„测的综åˆæ•°æ®ã€‚该地区的许多地区也缺ä¹å…³é”®çš„IT基础设施。2016年,åªæœ‰ä¸åˆ°ä¸€åŠçš„亚洲人å£ä½¿ç”¨äº’è”网,其ä¸åŒ…括大多数东盟国家的多数人å£ã€‚
东盟国家å¯ä»¥é¦–先利用现有技术,更易于实施的方法,以改善教育的质é‡å’Œå…¬å¹³æ€§ã€‚åƒå¯æ±—å¦é™¢(Khan?Academy)或马æ¥è¥¿äºšäºšæ´²ç”µå大å¦(Asia?e?university)è¿™æ ·çš„åœ¨çº¿è‡ªå¦è¯¾ç¨‹æ高了入å¦çš„机会。通过é…备预装æ料和低带宽通é“的设备,在å远地区或缺ä¹ç†Ÿç»ƒæ•™å¸ˆçš„地方,教育质é‡å’Œå…¬å¹³æ€§å¾—到了改善。
这些工具并ä¸èƒ½ä¿è¯æ›´å¥½çš„教育æˆæžœã€‚政ç–制定者和地方行政官员必须调整政ç–,以满足å¦ç”Ÿçš„实际需求,并切实地考虑基础设施的准备和规划。教育科技解决方案应该专注于教å¦ï¼Œå°†æŠ€æœ¯è§£å†³æ–¹æ¡ˆä¸ŽçŽ°åœºæ•™å¦çš„优势结åˆèµ·æ¥ï¼Œå¹¶ä¸Žæœ¬åœ°é€‚用的课程相匹é…。建立一项能够评估国家系统å¯è¡Œæ€§å’Œæ€§èƒ½çš„教育科技政ç–,将å…许å„国在时机æˆç†Ÿçš„时候充分利用人工智能。
类似地,å„国现在å¯ä»¥å¼€å§‹ä¸ºäººå·¥æ™ºèƒ½æŠ€æœ¯çš„å‘展åšå‡†å¤‡ï¼Œå¼€å‘更完备的国家数æ®åº“,更先进的技术解决方案ä¾èµ–于æ¤ã€‚这包括获å–å¦ç”Ÿäººå£ç»Ÿè®¡æ•°æ®ã€çŽ¯å¢ƒå˜é‡ã€å‡ºå‹¤çŽ‡ã€å¦æ ¡å±žæ€§ã€ä¸ªäººã€å¦æ ¡å’Œåœ°åŒºå…³ç³»çš„æ•°æ®ã€‚政府ä¸éœ€è¦è‡ªå·±æ”¶é›†å’Œæ•´ç†æ•°æ®ï¼›ä»–们å¯ä»¥ä¸Žå›½é™…或当地公å¸åˆä½œã€‚然而,政府需è¦å‚与其ä¸ï¼Œå› 为它们往往是主è¦çš„æ•°æ®æ”¶é›†è€…,必须确ä¿æ•°æ®éšç§ã€‚
一旦这些数æ®ç»“æž„å°±ä½ï¼Œæœºå™¨å¦ä¹ 算法——包括那些在该地区以外开å‘的算法——就å¯ä»¥åœ¨å›½å®¶å±‚é¢ä¸Šå¦ä¹ 。这将为教育部门æ供如何部署教育资æºå’Œè°ƒæ•´æ”¿ç–以满足劳动力需求的å®è´µæŒ‡å¯¼ï¼Œç›®å‰è¿˜æ²¡æœ‰å“ªä¸ªä¸œç›Ÿå›½å®¶èƒ½å¤Ÿå®žæ–½ã€‚在个人层é¢ï¼Œå›½å®¶å±‚é¢çš„æ•°æ®å¯ä»¥æ”¯æŒå¹¶æŒ‡å¯¼æ•™å¸ˆã€å®¶é•¿å’Œç®¡ç†è€…如何让å¦ç”Ÿç•™åœ¨å¦æ ¡ï¼Œä»¥åŠé‡‡å–ä»€ä¹ˆæ ·çš„å¹²é¢„æŽªæ–½æ¥é™ä½Žå¦ç”Ÿå¤±å¦çš„风险。
解决跨领域的挑战和机é‡
æ£å¦‚上é¢è®¨è®ºçš„行业例å所示,人工智能å¯ä»¥æžå¤§åœ°æ高生产力。如今,ä¼ä¸šå¯ä»¥ä½¿ç”¨å¼ºå¤§è€Œæˆç†Ÿçš„分æžå·¥å…·ï¼Œä»Žè€Œæ高è¿è¥ç»©æ•ˆï¼Œåˆ›é€ 新的市场机é‡ã€‚
但这并ä¸æ˜¯ä¸€ä¸ªç®€å•çš„命题——没有一个å•ç‹¬çš„组织能够独自解决围绕这些技术的所有问题。有å¤æ‚的伦ç†ã€æ³•å¾‹å’Œå®‰å…¨é—®é¢˜æœ‰å¾…回ç”,而最终对就业的影å“ä»æœ‰å¾…观察。整个东盟地区将需è¦åŠ 强其数å—基础设施建设,å‘展拥有先进数å—技能的更大的人æ‰åº“,并确ä¿å»ºç«‹ä¸€ä¸ªç»è¿‡æ·±æ€ç†Ÿè™‘的监管框架。æ£å¦‚我们在下é¢ç¬¬3节所讨论的,解决这些问题需è¦å…¬å…±å’Œç§è¥éƒ¨é—¨çš„åˆä½œå’Œå…±åŒåŠªåŠ›ã€‚
今天,东盟的大部分地区在数å—æ™®åŠæ–¹é¢è½åŽäºŽå…¶ä»–国家。但这并ä¸æ˜¯è¯¥åœ°åŒºçš„å…¬å¸è®¤ä¸ºä¸‹ä¸€ä»£æŠ€æœ¯ä¸Žæœ¬åœŸå¸‚åœºæ²¡æœ‰ç›¸å…³æ€§ã€‚äº‹å®žä¸Šï¼Œä¸€äº›æŠ€æœ¯æ¬ å‘达的地区å¯èƒ½å•è‚²ç€ä¸€äº›æœ€æœ‰å‰é€”的机é‡ã€‚它们å¯ä»¥ä»Žä¸€ä¸ªå…¨æ–°çš„领域开始å‘展,它们ä¸å¤ªä¼šè¢«é—ç•™ç³»ç»Ÿå’Œè§„ç« åˆ¶åº¦æ‰€å›°ã€‚çµæ„Ÿå¯ä»¥ä»Žä¸å›½èŽ·å¾—,ä¸å›½åœ¨éžå¸¸çŸçš„时间内æˆåŠŸå»ºç«‹äº†ä¸€ä¸ªå¼ºå¤§çš„æ•°å—生æ€ç³»ç»Ÿâ€”â€”è€Œåœ¨æ¬ å‘è¾¾ç»æµŽä½“ä¸ï¼Œä¸œç›Ÿçš„åˆåˆ›ä¼ä¸šä¹Ÿå¯èƒ½ä¼šè“¬å‹ƒå‘展。
三ã€ä¸œå—亚å‘展人工智能行业需è¦è§£å†³çš„关键问题æ£å¦‚其上所述,东å—亚ä¸åŒä¸šåŠ¡é¢†åŸŸçš„æ•°å—化æˆç†Ÿç¨‹åº¦å„有ä¸åŒã€‚如果å•çº¯ä¾é 市场的推动力é‡ï¼Œé‡‘èžæœåŠ¡ä¸šã€é«˜ç§‘技和电信行业的先驱者们或将最先接纳人工智能。然而,è¦æŠ“ä½äººå·¥æ™ºèƒ½çš„市场价值,并真æ£æ”¹å–„社会并éžæ˜“事。这将需è¦æ”¿ç–åˆ¶å®šè€…çš„ç»“æž„æ€§å¹²é¢„æŽªæ–½ï¼ŒåŠ ä¹‹è¡Œä¸šå‚与者的积æžæ‰¿è¯ºå’Œè·µè¡Œã€‚
以下我们将列举一些该地区在人工智能å‘展ä¸éœ€è¦è§£å†³çš„关键问题,åŒæ—¶æŽ¢è®¨æ”¿åºœå’Œä¼ä¸šå¯ä»¥åœ¨å…¶ä¸å‘挥的é‡è¦ä½œç”¨ã€‚
对于所有人工智能的å‘展潜力æ¥è¯´ï¼Œåœ¨æ²¡æœ‰äººç±»æŒ‡å¯¼çš„情况下让机器进行å¦ä¹ å’Œåšå‡ºå†³ç–,并对其进行管ç†æ˜¯ä¸€é¡¹è‰°å·¨çš„任务,也是一ç§é‡è¦è´£ä»»ã€‚这些技术æ£åœ¨æŠŠæ•´ä¸ªç¤¾ä¼šå¸¦å…¥æœªçŸ¥çš„å‘展方å‘。尽管我们知é“,人工智能应用程åºçš„增长需è¦åŸºäºŽæ•°æ®ç”Ÿæ€ç³»ç»Ÿå’Œæ•°å—能力的æŸäº›åŸºæœ¬è¦ç´ ,但我们ä¸çŸ¥é“人工智能技术进过第二和第三次è¿ä»£åŽä¼šå‡ºçŽ°ä½•ç§å•†ä¸šæ¡ˆä¾‹ï¼Œä¹Ÿä¸çŸ¥é“公众æ€åº¦ä¼šå‘生何ç§è½¬å˜ã€‚人工智能的普åŠè¿˜æ¶‰åŠåˆ°ä¸€äº›ç¤¾ä¼šä»·å€¼è§‚的问题,但这些问题没有任何确定性的ç”æ¡ˆã€‚å› æ¤ï¼Œæˆ‘们æ出一些开放性的问题,从而引入更多的深入讨论。
1ã€ç§è¥éƒ¨é—¨çš„å‘展路线
对于ä¼ä¸šæ¥è¯´ï¼Œäººå·¥æ™ºèƒ½çš„æ™®åŠéµå¾ªäº†å…¶ä»–æ•°å—技术å‘å±•çš„è·¯çº¿å›¾ã€‚è¿™äº›å…ƒç´ åŒ…æ‹¬æ˜Žç¡®å®šä¹‰çš„ç”¨ä¾‹æˆ–ä»·å€¼æº;å¥å£®çš„æ•°æ®ç”Ÿæ€ç³»ç»Ÿ;熟练使用系统和工具的雇员;ä¸Žæ ¸å¿ƒä¸šåŠ¡çš„å·¥ä½œæµè¿›è¡Œæœ‰åºæ•´åˆ;以åŠæŽ¥å—“测试和å¦ä¹ â€æ–¹æ³•çš„开放文化。对于整个东å—亚的ä¼ä¸šæ¥è¯´ï¼Œå³ä½¿æ˜¯åœ¨å‰æ²¿è¡Œä¸šï¼Œå…¶ä¸çš„æ•°æ®ç”Ÿæ€ç³»ç»Ÿã€è¿è¥æ–‡åŒ–和关键技能往往都å˜åœ¨ç€ä¸å°‘éšœç¢ã€‚
创建å¥å£®çš„æ•°æ®ç”Ÿæ€ç³»ç»Ÿ
对于人工智能技术æ¥è¯´ï¼Œå¿…须有稳定的å¯é ã€å¯æ“作和安全数æ®ï¼Œè¿™æ˜¯äººå·¥æ™ºèƒ½æŠ€æœ¯å¦ä¹ 和完善功能的基本方å¼ã€‚但东å—亚地区的多个行业在数æ®åŸºç¡€æ–¹é¢å˜åœ¨å¾ˆå¤šå›°éš¾ã€‚ç›®å‰å…¶ä¸çš„许多行业都缺ä¹è¶³å¤Ÿçš„å…³é”®ä¼ æ„Ÿå™¨ç³»ç»Ÿæ¥è·Ÿè¸ªæ“作数æ®ã€‚在æŸäº›æƒ…况下,人工智能程åºéœ€è¦ä¾æ‰˜å®žæ—¶æ•°æ®æµè¿›è¡Œå†³ç–和相关æ“作。例如,东å—亚的多家电信è¿è¥å•†å°†å®žæ—¶ç½‘络数æ®ä¼ 输到他们的数æ®åº“ä¸ï¼Œå¹¶åˆ©ç”¨è¿™äº›æ•°æ®æ¥å¼€å±•ä¸Žå®¢æˆ·å¯†åˆ‡ç›¸å…³çš„活动和通知。举一个简å•çš„例å,当用户在接近他的数æ®æµé‡ä¸Šé™æ—¶ä¼šæ”¶åˆ°ç›¸åº”通知。但åªæœ‰å°‘æ•°å‡ ä¸ªè¡Œä¸šå°†è¿™ç§ç±»åž‹çš„解决方案实现规模化应用。
å³ä½¿å¾ˆå¤šå…¬å¸è®¾ç½®äº†è¶³å¤Ÿçš„ä¼ æ„Ÿå™¨ï¼Œä½†å…¶ä¸å¾ˆå¤šä¾æ—§ç¼ºä¹åˆé€‚的基础设施æ¥å˜å‚¨æ•°æ®ï¼Œæ›´æ— 法将其èšåˆæˆå¯æ“作的数æ®å½¢å¼ç”¨äºŽç›¸åº”决ç–。在许多公å¸ä¸ï¼Œæ•°æ®å˜å‚¨éƒ½æ˜¯å„ä¸ç›¸å…³çš„å¤å²›ã€‚在å¦ä¸€äº›å…¬å¸ä¸ï¼Œäººä»¬æ”¶é›†äº†å¤§é‡çš„æ•°æ®ï¼Œä½†ä»Žæœªè¿›è¡Œæœ‰æ•ˆåˆ†æžã€‚éº¦è‚¯é”¡çš„ä¸€é¡¹ç ”ç©¶å‘现,石油钻井平å°ä¸Š3ä¸‡ä¸ªä¼ æ„Ÿå™¨æ•æ‰çš„全部数æ®ä¸ï¼Œåªæœ‰ä¸åˆ°1%被有效利用。
现在,éšç€åŸºäºŽäº‘æ•°æ®ç®¡ç†å¹³å°çš„出现,å˜å‚¨å’Œåˆ†æžæ•°æ®çš„æˆæœ¬æ£åœ¨ä¸æ–下é™ï¼Œæ•°æ®ä½¿ç”¨çš„便利性也在ä¸æ–æ高。许多ä¸å°ä¼ä¸šå’Œåˆ›ä¸šå…¬å¸éƒ½é‡‡ç”¨è¿™äº›æ–°æŠ€æœ¯å¹³å°æ¥é™ä½Žæˆæœ¬ï¼ˆè§èµ„æ–™4:“整åˆæ•°æ®ç–略需è¦å»ºç«‹ä¸€ä¸ªå¼ºå¤§çš„æ•°æ®ç”Ÿæ€ç³»ç»Ÿâ€ï¼‰ã€‚ä¸ºäº†å®žçŽ°ä»–ä»¬å…³äºŽäººå·¥æ™ºèƒ½çš„ç›®æ ‡ï¼Œå‚与者需è¦ç§¯æžæ‹¥æŠ±è¿™äº›æ–°æŠ€æœ¯ï¼ŒåŒæ—¶ç¡®ä¿æ£ç¡®çš„æ•°æ®ç®¡ç†èƒ½å¤Ÿåœ¨ä¸šåŠ¡ä¾¿æ·æ€§å’Œè§„模化之间实现平衡。
管ç†é£Žæ ¼å‘æ•°æ®é©±åŠ¨è¿‡æ¸¡
在ä¼ä¸šä¸å®žæ–½äººå·¥æ™ºèƒ½æ‰€éœ€è¦çš„æœ€æ ¹æœ¬æ–‡åŒ–å’Œç»„ç»‡è½¬å˜ï¼Œå°±æ˜¯è¦æŽ¥çº³æ•°æ®é©±åŠ¨å†³ç–。曾ç»å‡ç›´è§‰åšå‡ºçš„决ç–现在å¯ä»¥åŸºäºŽè¯æ®è€Œåšå‡ºï¼Œç”šè‡³å¯ä»¥æ˜¯è‡ªåŠ¨åŒ–的。由于人工智能在东å—亚地区ä»æ˜¯ä¸€ä¸ªç›¸å¯¹è¾ƒæ–°çš„概念,ä¼ä¸šä¹Ÿéœ€è¦é€æ¥é€‚应这ç§æ–°çš„模å¼ã€‚
å³ä½¿æ˜¯é‚£äº›å¯¹æ•°æ®æ‰‹æœºå’Œæ•°æ®åˆ†æžè¿›è¡ŒæŠ•èµ„çš„å…¬å¸ï¼Œä¹Ÿå¯èƒ½æ— 法在决ç–过程ä¸æœ‰æ•ˆä½¿ç”¨æ•°æ®ã€‚å…¶ä¸åŒ…括以下一些问题:
(1)对业务情况和价值æ¥æºçš„表述ä¸åˆ°ä½ï¼Œå¯¼è‡´å†³ç–基础薄弱。
(2)ä¸å±‚管ç†äººå‘˜ç¼ºä¹ç›¸åº”的能力建设,ä¸æ„¿æ„ä¾é 人工智能的分æžä½œä¸ºå†³ç–çš„ä¾æ®ã€‚
(3)对雇员特别是对一线工作者的å†åŸ¹è®æŠ•èµ„有é™ã€‚
(4)缺ä¹é›‡å‘˜å¼•å…¥æœºåˆ¶ã€‚
(5ï¼‰ä¸Žæ‰€æœ‰æ–‡åŒ–è½¬åž‹ä¸€æ ·ï¼Œé¢†å¯¼åŠ›å¯¹äºŽäººå·¥æ™ºèƒ½çš„æˆåŠŸå®žæ–½è‡³å…³é‡è¦ã€‚麦肯锡全çƒç ”究所的一项调查å‘现,那些æˆåŠŸéƒ¨ç½²äº†äººå·¥æ™ºèƒ½æŠ€æœ¯çš„å…¬å¸å—访者表示,相比于那些没有采用任何人工智能技术的公å¸ï¼Œå…¶é«˜ç®¡å±‚的支æŒåº¦å‡ 乎是其他公å¸çš„两å€ã€‚
资料4:整åˆæ•°æ®ç–略需è¦å»ºç«‹ä¸€ä¸ªå¼ºå¤§çš„æ•°æ®ç”Ÿæ€ç³»ç»Ÿ
æ•°æ®æ£åœ¨æˆä¸ºä¸€ç§æ–°çš„资本形å¼ã€‚è·¨è¡Œä¸šç ”ç©¶æ˜¾ç¤ºï¼Œå¹³å‡è€Œè¨€ï¼Œåœ¨å†³ç–过程ä¸ä»…有ä¸åˆ°ä¸€åŠçš„组织结构数æ®è¢«ç”¨äºŽå†³ç–,超过70%的员工获得的数æ®æ˜¯ä¸å¿…è¦çš„,而数æ®åˆ†æžå¸ˆ80%的时间是用于å‘现和准备数æ®çš„。
ä¼ä¸šéœ€è¦é‡‡å–一ç§ç¨‹åºåŒ–的方法æ¥æž„建数æ®èµ„产,并在所有业务部门的支æŒä¸‹ï¼Œåˆ©ç”¨è¿™äº›èµ„产æ¥æ”¹å˜æ•´ä¸ªä¼ä¸šã€‚以下是这类数æ®é©±åŠ¨è½¬å˜çš„三个关键组æˆéƒ¨åˆ†ï¼š
一个清晰的数æ®æˆ˜ç•¥ï¼Œå¾€å¾€ä¸Žä¼ä¸šçš„愿景紧密相连
(1)第一æ¥æ˜¯å¼„清数æ®å¦‚何被用æ¥æŽ¨åŠ¨å…³é”®çš„ä¸šåŠ¡ç›®æ ‡å’Œæ–‡æ¡£ç”¨ä¾‹çš„å®žçŽ°ã€‚
(2)下一个问题是,è¦ç¡®å®šä¼ä¸šæ•°æ®çš„关键缺å£ï¼Œéœ€è¦ç”¨æ–°çš„集åˆç³»ç»Ÿæˆ–互补的外部数æ®åŠ 以填补;ä¼ä¸šä¹Ÿåº”该对æ供独特优势的专有数æ®èµ„产ä¿æŒå¼€æ”¾çš„æ€åº¦ã€‚
(3)将简å•çš„æˆæœ¬æ•ˆç›Šåˆ†æžä¸Žæ¯ä¸ªç”¨ä¾‹è”系起æ¥ï¼Œæœ‰åŠ©äºŽè¯„估它们对业务的é‡è¦æ€§ï¼Œå¹¶æŒ‡å¯¼è¯¸å¦‚“外采或开å‘â€ä¹‹ç±»çš„决ç–。
æ•°æ®æž¶æž„和路线图实现的总体è“图
(1)数æ®æž¶æž„的设计æºäºŽç¬¦åˆå…¬å¸éœ€æ±‚çš„æ•°æ®æ¨¡åž‹è§†å›¾ä»¥åŠä¼˜å…ˆçº§ç”¨ä¾‹ã€‚
(2ï¼‰è¯¥æž¶æž„çš„è®¾è®¡ç›®æ ‡æ˜¯ä¼˜åŒ–æ•°æ®æ”¶é›†ã€èšåˆã€ä½¿ç”¨å’ŒåŽç»æ›´æ–°ï¼ŒåŒæ—¶ä¿æŒæ•°æ®å‡†ç¡®æ€§å’Œä¸€è‡´æ€§ï¼Œç¡®ä¿æ•°æ®çš„安全性。
(3)选择åˆé€‚的技术能够控制å‡çº§ç³»ç»Ÿçš„æˆæœ¬ï¼ŒåŒæ—¶ä¸ºç³»ç»Ÿè¿è¡Œæ供足够的çµæ´»æ€§ã€‚
达到æŒç»æ€§å†³ç–和丰富数æ®é›†çš„有效数æ®æ²»ç†
(1)数æ®æ²»ç†æœºåˆ¶çš„本质是选择集ä¸çš„ã€è”åˆçš„ã€æˆ–完全去ä¸å¿ƒåŒ–çš„æ•°æ®ç»„织,以åŠé¦–å¸æ•°æ®å®˜åœ¨æ ¸å¿ƒç®¡ç†ä¸çš„ä½ç½®ã€‚
(2ï¼‰æ ¹æ®æ•°æ®åŠå…¶æ¥æºçš„é‡è¦æ€§ï¼Œå®šä¹‰ä¸Žå¤–部å„方的数æ®è¿›è¡Œäº¤äº’和共享的规则。
(3)制定了相关的指导方针,以开å‘能够对数æ®è¿›è¡Œé˜é‡Šçš„硬资产,比如ä¼ä¸šæ•°æ®è¯å…¸å’Œç›‘控数æ®è´¨é‡çš„仪表类应用。
æ‰“é€ æ£ç¡®çš„技能组åˆ
å„个公å¸å‡è¡¨ç¤ºï¼Œåœ¨è¯•å›¾å°†æ•°æ®å’Œç›¸å…³åˆ†æžæ•´åˆåˆ°çŽ°æœ‰ä¸šåŠ¡çš„过程ä¸ï¼Œæ‰¾åˆ°åˆé€‚的人选是他们é¢ä¸´çš„最大障ç¢ã€‚
麦肯锡最近的一项调查显示,大约有一åŠçš„ä¼ä¸šé«˜ç®¡è®¤ä¸ºæ‹›å‹Ÿä¸€ååˆæ ¼çš„æ•°æ®åˆ†æžäººæ‰éš¾ä¸ŠåŠ 难。尤其是对数æ®ç§‘å¦å®¶çš„需求é‡æ›´å¤§ã€‚而æ°æ°è¿™äº›äººå°±æ˜¯è®¾è®¡ã€å¼€å‘ã€éƒ¨ç½²å’ŒåŸ¹è®äººå·¥æ™ºèƒ½æŠ€æœ¯çš„人。目å‰è¿™ç±»äººæ‰éžå¸¸çŸç¼ºï¼Œå³ä¾¿æ˜¯åœ¨åƒç¡…è°·è¿™æ ·çš„å…¨çƒæ€§äººå·¥æ™ºèƒ½ä¸å¿ƒä¹Ÿæ˜¯å¦‚æ¤ã€‚而东å—亚这类人æ‰çš„çŸç¼ºæ›´ä¸ºä¸¥é‡ã€‚
å¦ä¸€ä¸ªåŒæ ·é‡è¦çš„角色是商业翻译,他们å¯ä»¥å……当分æžäººæ‰å’Œå®žé™…应用之间的纽带和桥æ¢ã€‚除了精通数æ®ï¼Œå•†ä¸šç¿»è¯‘还需è¦å…·å¤‡æ·±åŽšçš„组织架构知识ã€è¡Œä¸šæ–¹é¢æˆ–业务方é¢çš„专长。他们能够å‘æ•°æ®ç§‘å¦å›¢é˜Ÿæ出æ£ç¡®çš„问题,并从他们的分æžä¸èŽ·å¾—æ£ç¡®çš„è§è§£ã€‚
当然,公å¸ä¹Ÿå¯ä»¥é€‰æ‹©æŠŠæ•°æ®åˆ†æžä¸šåŠ¡è¿›è¡Œå¤–包,但对于商业翻译这ç§è§’色æ¥è¯´ï¼Œå…¶å¯ä»¥åˆ©ç”¨è‡ªå·±çš„专有知识深入组织架构的内部。而很多ä¼ä¸šæ‰€éœ€è¦æ˜¯ä»Žå†…éƒ¨æ‰“é€ ç›¸åº”èƒ½åŠ›ã€‚å¯¹äºŽä¼ä¸šæ¥è¯´ï¼Œå…¶ä¸ä¸€ç§é€‰æ‹©æ˜¯â€œæž„建-æ“作-转让â€æ¨¡å¼ï¼Œå³æ¥è‡ªå¤–部专业公å¸çš„专家被整åˆè¿›è·¨èŒèƒ½é¡¹ç›®å›¢é˜Ÿä¸ã€‚这些专家会与内部员工进行紧密åˆä½œï¼Œå…¶å‘员工æ供关于如何与人工智能技术系统进行åˆä½œçš„诀çªï¼ŒåŒæ—¶å‘˜å·¥ä¼šåˆ©ç”¨è‡ªèº«çš„è¿è¥ç»éªŒæ¥åŠ 深专家对公å¸çœŸå®žéœ€æ±‚çš„ç†è§£ã€‚而员工也相应获得了新技能,能够在åˆå§‹é˜¶æ®µä¹‹åŽä¸æ–自我æ高和完善。
2ã€æ”¿ç–制定者é¢ä¸´çš„结构性挑战
ç›®å‰ï¼Œä¸œå—亚的政ç–制定者需è¦é€šè¿‡åˆç†æ”¿ç–将现有创新转化为å¯æŒç»å¢žé•¿ã€‚政府å¯ä»¥é€šè¿‡å»ºç«‹åšå®žçš„政ç–åŸºå‚¨è®¾å®šæœ‰æŠ±è´Ÿæ€§çš„ç›®æ ‡ã€åˆºæ¿€ç§è¥éƒ¨é—¨çš„创新并采纳人工智能æ¥æŽ¨åŠ¨è¿™ä¸€è½¬åŒ–。
支æŒå¼€å‘和采纳人工智能的政ç–
东å—亚å¯ä»¥é€šè¿‡åœ°åŒºæ”¿ç–而éžæœ¬åœ°åŒ–政ç–æ¥æŽ¨åŠ¨äººå·¥æ™ºèƒ½çš„å‘展和普åŠã€‚最é‡è¦çš„任务之一是建立一个开放但安全的数æ®çŽ¯å¢ƒï¼Œè¿™æ˜¯æ•°å—以åŠäººå·¥æ™ºèƒ½æŠ€æœ¯çš„ç”Ÿå‘½çº¿ã€‚æˆ‘ä»¬çš„ç ”ç©¶æ˜¾ç¤ºï¼Œä¸œå—亚地区的æµåŠ¨æ€§å…·æœ‰é«˜åº¦çš„å…¨çƒè”系,包括商å“å’ŒæœåŠ¡è´¸æ˜“ã€äººå‘˜æµåŠ¨å’Œèµ„本æµåŠ¨éƒ½æ˜¯å¦‚æ¤ã€‚但在跨境数æ®æµåŠ¨æ–¹é¢ï¼Œä¸œç›Ÿçš„å…¨çƒè”系明显较少(表6)。构建该地区的数å—基础设施是关键的一æ¥ï¼Œè€Œæ•°æ®æ²»ç†æ˜¯å…¶ä¸çš„æ ¸å¿ƒç»„æˆã€‚
跨太平洋伙伴关系å定(TPP)为东盟解决数æ®äº¤æµéšœç¢æ供了一个机会,而且它æ出的一些框架å¯ä»¥åœ¨åœ°åŒºå±‚é¢è¿›è¡Œè€ƒè™‘。 These include:
(1ï¼‰åˆ¶å®šæ ‡å‡†ï¼Œä¿æŠ¤æ¶ˆè´¹è€…ä¸å—网络诈骗的侵害,并明确个人信æ¯å°†å¦‚何跨界交æµã€‚
(2)防æ¢å’Œåº”对ä¸æ–å˜åŒ–的网络安全å¨èƒã€‚
(3)ä¿æŠ¤æ•°å—知识产æƒï¼ŒåŒæ—¶å‡å°‘æµ·å…³ã€äº’è”网接å£ã€äº§å“æ§è§†ç‰å¯¹åœ¨çº¿å•†åŠ¡é€ æˆçš„éšœç¢ã€‚
(4)é¿å…“数æ®ä¿æŠ¤ä¸»ä¹‰â€ï¼Œè§„范ä¼ä¸šæ•°æ®å˜å‚¨ã€‚
政府也å¯ä»¥é€šè¿‡è®©è‡ªå·±çš„公共数æ®æ›´æ˜“äºŽè®¿é—®ï¼Œä»Žè€Œå»ºç«‹æ›´åŠ å¼€æ”¾çš„æ•°æ®ç”Ÿæ€ç³»ç»Ÿã€‚è¿™å¯ä»¥ä¸ºç¬¬ä¸‰æ–¹åº”用ã€äººå·¥æ™ºèƒ½å¼€å‘者和创业公å¸æ供丰富的开å‘模å—。
éšç€äººå·¥æ™ºèƒ½ä¸æ–出现新用途,政府和整个社会也需è¦åŠªåŠ›è§„范数æ®éšç§çš„原则。如果政府和ä¼ä¸šæ”¶é›†çš„æ•°æ®è¢«åŒ¿å化,公众还有æƒçŸ¥é“他们的数æ®æ˜¯å¦‚何被使用的å—?那些人工智能的用户有义务去解释他们的机器是å¦ç¬¦åˆå…¬ä¼—利益或个人幸ç¦å—?
å„å›½æ”¿åºœè¿˜å¿…é¡»è€ƒè™‘è‡ªèº«åœ¨è§£å†³æŠ€æœ¯é¢ è¦†å¸¦æ¥çš„è´Ÿé¢æ•ˆåº”æ–¹é¢æ‰€å‘挥的作用。其ä¸ä¸€é¡¹ä¸»è¦æˆ˜ç•¥å°†æ˜¯é•¿æœŸæŠ•èµ„教育,其ä¸ä¹ŸåŒ…括继ç»æ•™è‚²ä½“系,从而帮助处于èŒä¸šç”Ÿæ¶¯ä¸æœŸçš„劳动者跟上数å—ç»æµŽä¸æ–å˜åŒ–的需求。但这åŒæ ·ä¼šå¼•å‘许多问题。政府如何确ä¿å¦‡å¥³å’Œå†œæ‘人士能够平ç‰åœ°æŽ¥å—æ•°å—化培è®ï¼Ÿä»–们能å¦åœ¨ä¸€å®šç¨‹åº¦ä¸ŠæŠµæ¶ˆæ•°å—é¢ è¦†å¸¦æ¥çš„ä¸å¹³ç‰æ‰©å¤§ç‰é£Žé™©ï¼Ÿå“ªäº›è¡Œä¸šæœ€é€‚åˆè¢«é¢ 覆?政府和公å¸åº”该如何分é…å†åŸ¹è®çš„责任?人工智能技术本身能够æ供部分解决方案å—?
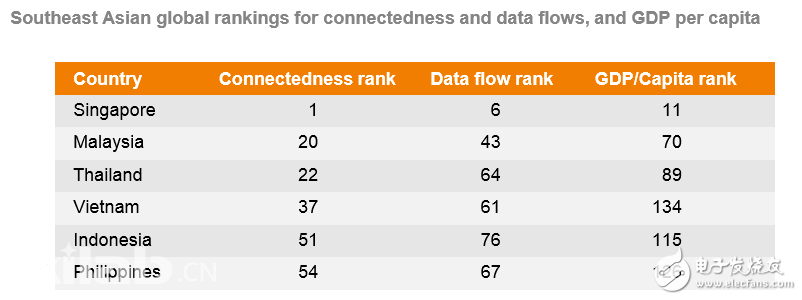
图表6:东å—亚地区的è”ç³»ã€æ•°æ®æµé‡ä»¥åŠäººå‡å›½å†…生产总值的排å。
在东å—亚国家之间,基于贸易和资金æµçš„ä¼ ç»Ÿé¢†åŸŸé«˜åº¦äº’è”,但相关之间的数æ®æµè”ç³»å´ä¸é‚£ä¹ˆç´§å¯†ã€‚
政府å¯ä»¥åˆ©ç”¨è´¢æ”¿æ”¿ç–æ¥è§£å†³å¤±ä¸šå’Œç¤¾ä¼šæ··ä¹±é—®é¢˜ã€‚但除了æ供资金的安全ä¿éšœå¤–,还有其他方法å¯ä»¥åˆ©ç”¨æŠ€æœ¯æ¥é™åˆ¶å¤±ä¸šå—?如果一个由人工智能推动的ç»æµŽéœ€è¦æ›´å°‘的劳动力,那么是å¦æœ‰å¯èƒ½é€šè¿‡è®¾è®¡è®©å·¥ä½œå®‰æŽ’æ›´åŠ çµæ´»ï¼Œè®©å…¬å¸èƒ½å¤ŸååŒå·¥ä½œï¼Ÿ
最åŽï¼Œç”±äºŽæ—©æœŸé‡‡ç”¨è€…ç´§æ¡äººæ‰ã€å…¼å¹¶æ›´å°çš„创新者ã€å¹¶èŽ·å¾—ä¸æˆæ¯”例的ç»æµŽåˆ©æ¶¦ï¼Œäººå·¥æ™ºèƒ½è¡Œä¸šå˜åœ¨ç€å¸‚场垄æ–的风险。但这ç§å¯èƒ½æ€§ç›®å‰è¢«å¤§åž‹è·¨å›½å…¬å¸åœ¨è¯¥åœ°åŒºçš„æŠ€æœ¯æ‰©å¼ ä»¥åŠæ™®åŠæ‰€å¸¦æ¥çš„益处所抵消。
当政府通过监管或财政政ç–进行干预时,应
The latest Windows has multiple versions, including Basic, Home, and Ultimate. Windows has developed from a simple GUI to a typical operating system with its own file format and drivers, and has actually become the most user-friendly operating system. Windows has added the Multiple Desktops feature. This function allows users to use multiple desktop environments under the same operating system, that is, users can switch between different desktop environments according to their needs. It can be said that on the tablet platform, the Windows operating system has a good foundation.
Windows Tablet,New Windows Tablet,Tablet Windows
Jingjiang Gisen Technology Co.,Ltd , https://www.gisentech.com