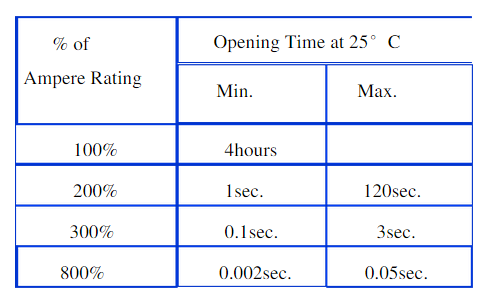
A good or suitable fuse should comply with at least three requirements: The break must be broken, it should not be broken, the break must be safe. The first function of the fuse is the protection function, that is, the fuse should play a role when it needs protection. This is the first thing we need to consider when choosing a fuse. Under normal circumstances, the rated current of the fuse must be greater than the normal operating current of the circuit, and has a certain overload capacity, but if the margin is too large, it will reduce or weaken the protection function, the fuse should not act when the action, resulting in being protected The damage to the components is even more serious and dangerous. The main reference tool for designers when selecting fuses is the "time-current characteristic curve" in the product specifications provided by the fuse manufacturer. Since the melting time reflected on the curve is under normal atmospheric conditions, we also need to properly consider the influence of the ambient temperature, etc. when necessary. Selecting the type of fuse with the proper fuse characteristics and proper current rating will meet the fuse protection function. The second function of the fuse is to carry the function, which is also known as the ability to withstand the pulse. This is an important issue that we must consider when selecting the fuse. In the process of fuse use, the chance of normal current fluctuations or transient pulses is much greater than the fault overcurrent, so in a sense, this consideration is particularly important and practical for the use of the fuse. As long as the fuse's heat of fusion I2t is greater than the energy of the circuit pulse, the fuse can withstand. The "time-melting thermal curve" is a tool that provides the designer with the ability to use the fuse when using a fuse (again, the current-melting heat curve can also be used. In the form of), to further see that the fuse will suffer some damage even if it is not blown when subjected to pulse impact. In other words, the I2t of the fuse will be reduced, that is, the ability of the impulse resistance is reduced, so when selecting the fuse, The factor of this attenuation must also be taken into account. The usual simple calculation requires a 3-5 times margin to ensure that the fuse has sufficient pulse resistance. There is a contradiction between the pulse-resistant capability of a fuse and its protection performance. In these two aspects we must seek a reasonable balance to find the best combination. Select the type of fuse with the proper melting heat energy value and enlarge the enough and reasonable safety margin to meet the carrying function of the fuse (pulse resistance). The third function of the fuse is the safety function. High-quality and reliable fuses should ensure safety before and during their operation, that is, they can be safely conducted and safely blown. The main technical indicator that can guarantee this requirement of the fuse is the breaking capacity. The breaking capacity is the maximum current that the fuse can safely cut off the circuit. In general, it refers to the short-circuit current. That is, the fuse must be able to break the circuit absolutely safely when it encounters a short-circuit current. That is, no unsafe factors, such as continuous arcing, multiple conduction, crushing, splashing, burning, and even explosion, will occur during the breaking process. The breaking capacity of each fuse must be equal to or greater than the maximum short-circuit current of the circuit being protected. The rated voltage of the fuse determines its withstand voltage and is another indicator of the safety performance of the fuse. It can only be used in circuits where the operating voltage is less than or equal to the rated voltage of the fuse. Safety certifications for safety components are made in countries and regions around the world, and the safety certification of fuses is also essential for its safety functions. Select the type of fuse with sufficient breaking capacity and rated voltage and obtained the necessary safety certification for the application area to meet the safety function of the fuse. In summary, the appropriate fuse characteristics and rated current; adequate and reasonable melting heat value; and appropriate breaking capacity, rated voltage and safety certification are necessary conditions to ensure the main functions of the fuse, only if these three conditions are met. On the basis of the simultaneous coordination of the constraints between the protection performance and the impulse withstand capability, the most reasonable balance is achieved, and we are only able to make a judgment: such fuses are high quality and reliable fuses. 1. Rated current---In â— The rated current of the fuse refers to its nominal rated current, which is usually the maximum current the circuit can operate. â— The correct selection of the rated current of the fuse must be considered as follows: â— For example: Operating current of the circuit: Ir = 1.5 A, â— The UL rated fuse current rating should be: In = Ir/Of = 1.5/0.75 = 2Az Here, Ir is the circuit operating current, and Of is the UL specification fuse reduction rate. â— So choose 2A fuse â— There is no reduction rate requirement for IEC size fuses, ie: Ir = In z If the special rated current is not universal, the nearest higher value should be selected. â— Wrong choice: Use the current value of the desired fuse as the rated current value 2. Rated voltage---Un â— The rated voltage of the fuse refers to its nominal rated voltage, which is usually the maximum voltage that the fuse can withstand after it is disconnected. â— When the fuse is energized, the voltage applied to both ends is much less than its rated voltage, so the rated voltage is basically irrelevant. â— The correct choice of fuse rated voltage should be equal to or greater than the circuit voltage z. For example: 250V fuse can be used for 125V circuit â— For low-voltage electronics applications, an AC rated fuse can be used in DC circuits. â— Regarding the rated voltage of the fuse should be considered: When the circuit voltage does not exceed the rated voltage of the fuse, the fuse is capable of breaking the maximum current given â— Misunderstandings: The rated voltage of the fuse must be the same as the circuit voltage! 3. Ambient temperature â— The small ambient temperature or known operating temperature of the fuse, which affects the operation of the fuse. z The higher the ambient temperature, the hotter the fuse will work and the shorter its lifespan. â— Regardless of the UL specification or the IEC specification, the indicators of the fuse are all at 25 °C. If the operating temperature of the small environment is high, the temperature of the fuse should be taken into consideration. â— Example: Use a fast-acting fuse to operate under a small 90°C environment and 1.5A current. If an IEC-rated fuse is selected, the rated current is: In = In/ Tf = 1.5A/0.95 = 1,58 A Recommended 1.6 A or 2 A Fuses If UL fuse is selected, the rated current is: In = In/OfxTf = 1.5A/0.75x0.95 = 2.1 A fuse of 2.5 A should be selected 4. Voltage drop/cold resistance---Ud/R â— In general, the resistance of a fuse is inversely proportional to its rated current. â— In the protection circuit, the smaller the fuse resistance, the better, so that its power loss is small; therefore, the maximum voltage drop value or cold resistance value is specified in the fuse technical parameters, but it is not used as a basis for product acceptance. â— Voltage drop of the fuse: The rated value of the DC current is used to allow the fuse to reach the thermal equilibrium. â— Cold resistance of the fuse: reading measured at less than 10% of the rated current z The voltage drop and the cold resistance of the fuse can be mutually converted. â— The voltage drop of the small-size fuse has a greater impact on the low-voltage circuit. Be careful! z In extreme cases, the required operating current cannot be output due to too high resistance. 5. Fusing characteristics â— Also known as the time-current characteristic or the IT characteristic or the ampere-second characteristic of the fuse, it is the main electrical performance indicator of the fuse. It indicates the time range for the fuse to be blown under different overload current loads. z When the current flowing through the fuse exceeds the rated current, the temperature of the melt gradually rises, and finally the fuse is blown, and we classify this as an overload condition. â— The fuse needs a certain overload capacity: The maximum non-blown current of the UL specification fuse is 110%In; the maximum non-fuse current of the IEC specification fuse is 150% In or 120% Inz. The fuse also requires timely blowout when exceeding the limited overload current: The UL specification fuse has a minimum fuse current around 130% In; the IEC specification fuse has a minimum fuse current around 180% In. â— According to different fuse characteristics, fuses can be divided into fast type and time delay type: â— Fast fuses are commonly used in resistive circuits to protect components that are particularly sensitive to current fluctuations; â— Time-delay fuses are commonly used in inductive or capacitive circuits with large inrush currents when the circuit state changes. They can withstand the impact of surge pulses when switching on and off, and can still be quickly disconnected when a true fault occurs. Each curve represents the fuse characteristics of a size fuse, and it can be found for each of the load currents. â— Different types of fuses have different shape characteristics. The time/current characteristic curve best describes the overload performance of the fuse, which is the main reference for the designer to choose the fuse specification. Time-current characteristics table It is usually stipulated that several fuses in the curve are used to check the fuse overload performance. Is the main basis for the quality assessment or acceptance of the fuse. 6. Breaking capacity---Ir â— Breaking capacity is also called maximum breaking capacity or short-circuit breaking capacity or breaking current. â— Breaking capacity is the main safety factor of the fuse. It shows the maximum current that the fuse can safely cut off at the specified voltage. â— When the current flowing through the fuse is large enough to short-circuit, the fuse is required to break the circuit safely without any destructiveness. â— When the rated breaking current value is exceeded, the fuse may break, explode, splash, and cause unsafe phenomena such as burning or destruction of the surrounding person or other components. â— The breaking capacity of the fuse depends on the structure of the fuse and the material used. In general, most of the low breaking capacity fuses are made of glass. The high breaking capacity fuses usually have a ceramic housing, and many of them are filled with pure particles. Quartz material â— As a rule, when the protected system is directly connected to the power input circuit and the fuse is placed in the power input section, a high breaking capacity fuse must be used. â— In most secondary circuits, especially when the voltage is lower than the supply voltage, the use of a low breaking fuse is sufficient. 7. Fusion Heat Value - I2t â— The melting heat energy (If2t) of the fuse refers to the energy required for the melt to melt. It is usually used as a technical indicator of the surge capacity of the fuse, where I is the overload current and t is the time of the fuse. The energy value (Ir2t) released during the flood â—Principle: If2t>Ir2t must be considered when selecting the fuse, that is, the heat of fusion of the fuse should be greater than the heat energy released by the inrush current. â— The fuse blowing time is related to the heat generated by the current, the heat dissipation conditions, and the heat capacity of the fuse. Many factors will affect the fuse blowing time. Therefore, the fuse will have different breaking current or breaking time. If2t, that is, if2t is not a constant â— The energy/time curve best describes the change of the fusion heat energy of the fuse, which is the main reference for the designer to choose the fuse resistance to pulse. â— Impulse impulse • When If2t > Ir2t, the fuse should be able to withstand the impact of a pulse. It will not be blown but will suffer some damage, thus slightly reducing its If2t â— By calculating and selecting the relationship between If2t and Ir2t, you can know the number of pulses the fuse can withstand. Conversely, if the fuse needs to withstand more than one surge, you must select If2t of the fuse and Ir2t of the circuit pulse. â— Presumed relationship between If2t and Ir2t of AEM fuses Ir2t <= 30% If2t 100,000 times Ir2t <= 38% If2t 10,000 times Ir2t <= 48% If2t 1,000 times â—About relationship between If2t and Ir2t of Littelfuse fuses Ir2t <= 22% If2t 100,000 times Ir2t <= 29% If2t 10,000 times Ir2t <= 38% If2t 1,000 times 8. Durability/life â— The life of the fuse is very long, almost in sync with the life of the device in the absence of failure â— Test the life of a small tubular fuse of the IEC specification by conducting it for one hour with a current of 1.20 In (or 1.05 In) under a DC power supply, disconnecting for 15 minutes, continuing for 100 cycles, and finally again with 1.5 In (or 1.15) In) The current is conducted for one hour without any fuse or other abnormality. â— The storage period of the fuse shall be no less than two years under normal conditions. The fuse may be stored again after passing the re-inspection. 9. Structural features and installation forms Structural features â— Tubular: glass tube - low breaking capacity, ceramic tube - high breaking capacity; Fine-grained quartz sand - used for arc extinguishing, glass tube discoloration - melting indication; Internal welding and external welding; Lead caps - for welding (sometimes lead forming first) ... â—Micro: Resistive, Transistor, Thin Film... â— Slice type: film type, multi-layer monolithic, resistance type... â—Other: Insert type, bolt type, sealed type, alarm type... â— Melt structure: round wire, flat wire, monofilament, double wire, composite wire; 10. Safety certification (do not explain) Mietubl Global Supply Chain (Guangzhou) Co., Ltd. , https://www.mietublmachine.com